Stress and the brain: Emotional support mediates the association between myelination in the right supramarginal gyrus and perceived chronic stress
- PMID: 36632310
- PMCID: PMC9826980
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2022.100511
Stress and the brain: Emotional support mediates the association between myelination in the right supramarginal gyrus and perceived chronic stress
Abstract
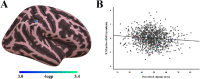
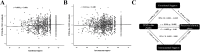
Perceived stress, which refers to people's evaluation of a stressful event and their ability to cope with it, has emerged as a stable predictor for physical and mental health outcomes. Increasing evidence has suggested the buffering effect of social support on perceived stress. Although previous studies have investigated the brain structural features (e.g., gray matter volume) associated with perceived stress, less is known about the association between perceived chronic stress and intra-cortical myelin (ICM), which is an important microstructure of brain and is essential for healthy brain functions, and the role of social support in this association. Using a sample of 1076 healthy young adults drawn from the Human Connectome Project, we quantified the ICMby the contrast of T1w and T2w images and examined its association with perceived chronic stress during the last month and social support. Behavioral results showed that perceived chronic stress was negatively associated with both emotional support and instrumental support. Vertex-wise multiple regression analyses revealed that higher level of perceived chronic stress was significantly associated with lower ICM content of a cluster in the right supramarginal gyrus (rSMG). Interestingly, the emotional support, but not the instrumental support, significantly mediated the association of perceived chronic stress with ICM in the rSMG. Overall, the present study provides novel evidence for the cortical myelination of perceived chronic stress in humans and highlights the essential role of the rSMG in perceived chronic stress and emotional support.
Keywords: Emotional support; Instrumental support; Intra-cortical myelin; Perceived chronic stress; Supramarginal gyrus.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors assert that they have no competing financial or personal interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The intracortical myelin content of impulsive choices: results from T1- and T2-weighted MRI myelin mapping.Cereb Cortex. 2023 May 24;33(11):7163-7174. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhad028. Cereb Cortex. 2023. PMID: 36748995 Free PMC article.
-
The Association between Body Mass Index and Intra-Cortical Myelin: Findings from the Human Connectome Project.Nutrients. 2021 Sep 16;13(9):3221. doi: 10.3390/nu13093221. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34579106 Free PMC article.
-
Altered Gray Matter Cortical and Subcortical T1-Weighted/T2-Weighted Ratio in Premature-Born Adults.Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2023 May;8(5):495-504. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsc.2022.02.013. Epub 2022 Mar 8. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2023. PMID: 35276405
-
Right supramarginal gyrus is crucial to overcome emotional egocentricity bias in social judgments.J Neurosci. 2013 Sep 25;33(39):15466-76. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1488-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24068815 Free PMC article.
-
Stress and the brain: Perceived stress mediates the impact of the superior frontal gyrus spontaneous activity on depressive symptoms in late adolescence.Hum Brain Mapp. 2019 Dec 1;40(17):4982-4993. doi: 10.1002/hbm.24752. Epub 2019 Aug 9. Hum Brain Mapp. 2019. PMID: 31397949 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Brain Iron Homeostasis and Mental Disorders.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Nov 13;12(11):1997. doi: 10.3390/antiox12111997. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38001850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interplay of academic procrastination, self-generated stress, and self-reported bruxism among medical and dental students: a cross-sectional study.BMC Psychol. 2024 Oct 23;12(1):586. doi: 10.1186/s40359-024-02105-w. BMC Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39443990 Free PMC article.
-
Intracortical myelin across laminae in adult individuals with 47,XXX: a 7 Tesla MRI study.Cereb Cortex. 2024 Aug 1;34(8):bhae343. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhae343. Cereb Cortex. 2024. PMID: 39183364 Free PMC article.
-
Mediating role of obesity on the association between disadvantaged neighborhoods and intracortical myelination.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 16:rs.3.rs-2592087. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2592087/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Commun Med (Lond). 2023 Sep 15;3(1):122. doi: 10.1038/s43856-023-00350-5. PMID: 36993600 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Mediation of the association between disadvantaged neighborhoods and cortical microstructure by body mass index.Commun Med (Lond). 2023 Sep 15;3(1):122. doi: 10.1038/s43856-023-00350-5. Commun Med (Lond). 2023. PMID: 37714947 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barth J., Schneider S., Von Känel R. Lack of social support in the etiology and the prognosis of coronary heart disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychosom. Med. 2010;72(3):229–238. - PubMed
-
- Bastos A.F., da Silva L.M., de Oliveira J.M., Oliveira L., Pereira M.G., Figueira I., Campos B. Beyond fear: patients with posttraumatic stress disorder fail to engage in safety cues. Journal of Affective Disorders Reports. 2022;10
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

