Novel Insights into The Roles of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) Modification and Autophagy in Human Diseases
- PMID: 36632456
- PMCID: PMC9830520
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.75466
Novel Insights into The Roles of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) Modification and Autophagy in Human Diseases
Abstract
Autophagy is an evolutionarily conserved cellular degradation and recycling process. It is important for maintaining vital cellular function and metabolism. Abnormal autophagy activity can cause the development of various diseases. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylation is the most prevalent and abundant internal modification in eukaryotes, affecting almost all aspects of RNA metabolism. The process of m6A modification is dynamic and adjustable. Its regulation depends on the regulation of m6A methyltransferases, m6A demethylases, and m6A binding proteins. m6A methylation and autophagy are two crucial and independent cellular events. Recent studies have shown that m6A modification mediates the transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of autophagy-related genes, affecting autophagy regulatory networks in multiple diseases. However, the regulatory effects of m6A regulators on autophagy in human diseases are not adequately acknowledged. In the present review, we summarized the latest knowledge of m6A modification in autophagy and elucidated the molecular regulatory mechanisms underlying m6A modification in autophagy regulatory networks. Moreover, we discuss the potentiality of m6A regulators serving as promising predictive biomarkers for human disease diagnosis and targets for therapy. This review will increase our understanding of the relationship between m6A methylation and autophagy, and provide novel insights to specifically target m6A modification in autophagy-associated therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Autophagy; Biomarkers; N6-methyladenosine (m6A); RNA modification; Therapeutic targets.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures





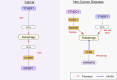
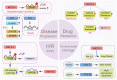
Similar articles
-
In Search of a Function for the N6-Methyladenosine in Epitranscriptome, Autophagy and Neurodegenerative Diseases.Neurol Int. 2023 Aug 10;15(3):967-979. doi: 10.3390/neurolint15030062. Neurol Int. 2023. PMID: 37606395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Emerging Role of N6-Methyladenosine RNA Methylation as Regulators in Cancer Therapy and Drug Resistance.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 6;13:873030. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.873030. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35462896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epitranscriptomic(N6-methyladenosine) Modification of Viral RNA and Virus-Host Interactions.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Nov 24;10:584283. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.584283. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33330128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current insights into the implications of m6A RNA methylation and autophagy interaction in human diseases.Cell Biosci. 2021 Jul 27;11(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s13578-021-00661-x. Cell Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34315538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA N6-methyladenosine methylation in post-transcriptional gene expression regulation.Genes Dev. 2015 Jul 1;29(13):1343-55. doi: 10.1101/gad.262766.115. Genes Dev. 2015. PMID: 26159994 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
M6A regulator methylation patterns and characteristics of immunity in acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 21;13(1):15688. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42959-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37735234 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulated FTO and ALKBH5 co-operatively activates FOXO signaling through m6A methylation modification in HK2 mRNA mediated by IGF2BP2 to enhance glycolysis in colorectal cancer.Cell Biosci. 2023 Aug 14;13(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-01100-9. Cell Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37580808 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Mechanisms in Osteoporosis: Exploring the Power of m6A RNA Modification.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Jan;29(1):e70344. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70344. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 39779466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Search of a Function for the N6-Methyladenosine in Epitranscriptome, Autophagy and Neurodegenerative Diseases.Neurol Int. 2023 Aug 10;15(3):967-979. doi: 10.3390/neurolint15030062. Neurol Int. 2023. PMID: 37606395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ALKBH5 facilitates the progression of skin cutaneous melanoma via mediating ABCA1 demethylation and modulating autophagy in an m6A-dependent manner.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Feb 25;20(5):1729-1743. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.92994. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38481816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dominissini D, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S, Schwartz S, Salmon-Divon M, Ungar L, Osenberg S. et al. Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature. 2012;485:201–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

