Neuropeptide Y protects kidney from acute kidney injury by inactivating M1 macrophages via the Y1R-NF-κB-Mincle-dependent mechanism
- PMID: 36632461
- PMCID: PMC9830509
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.80200
Neuropeptide Y protects kidney from acute kidney injury by inactivating M1 macrophages via the Y1R-NF-κB-Mincle-dependent mechanism
Abstract
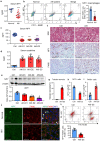
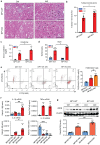
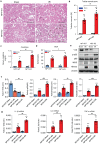
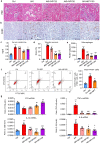
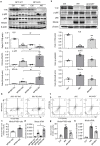
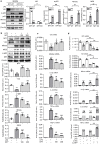
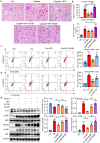
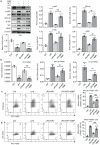
Neuropeptide Y (NPY) is produced by the nerve system and may contribute to the progression of CKD. The present study found the new protective role for NPY in AKI in both patients and animal models. Interestingly, NPY was constitutively expressed in blood and resident kidney macrophages by co-expressing NPY and CD68+ markers, which was lost in patients and mice with AKI-induced by cisplatin. Unexpectedly, NPY was renoprotective in AKI as mice lacking NPY developed worse renal necroinflammation and renal dysfunction in cisplatin and ischemic-induced AKI. Importantly, NPY was also a therapeutic agent for AKI because treatment with exogenous NPY dose-dependently inhibited cisplatin-induced AKI. Mechanistically, NPY protected kidney from AKI by inactivating M1 macrophages via the Y1R-NF-κB-Mincle-dependent mechanism as deleting or silencing NPY decreased Y1R but increased NF-κB-Mincle-mediated M1macrophage activation and renal necroinflammation, which were reversed by addition of NPY or by silencing Mincle but promoted by blocking Y1R with BIBP 3226. Thus, NPY is renoprotective and may be a novel therapeutic agent for AKI. NPY may act via Y1R to protect kidney from AKI by blocking NF-κB-Mincle-mediated M1 macrophage activation and renal necroinflammation.
Keywords: AKI; Inflammation; Macrophage; Mincle; Neuropeptide Y; Y1R.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Astragalus propinquus Schischkin and Panax notoginseng (A&P) compound relieved cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury through inhibiting the mincle maintained macrophage inflammation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Apr 24;252:112637. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112637. Epub 2020 Jan 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32004631
-
Curcumin relieved cisplatin-induced kidney inflammation through inhibiting Mincle-maintained M1 macrophage phenotype.Phytomedicine. 2019 Jan;52:284-294. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.09.210. Epub 2018 Sep 25. Phytomedicine. 2019. PMID: 30599909
-
Quercetin protects against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by inhibiting Mincle/Syk/NF-κB signaling maintained macrophage inflammation.Phytother Res. 2020 Jan;34(1):139-152. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6507. Epub 2019 Sep 9. Phytother Res. 2020. PMID: 31497913
-
The pattern recognition receptor, Mincle, is essential for maintaining the M1 macrophage phenotype in acute renal inflammation.Kidney Int. 2017 Mar;91(3):587-602. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.10.020. Epub 2016 Dec 22. Kidney Int. 2017. PMID: 28017324
-
Isorhamnetin ameliorates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in mice by activating SLPI-mediated anti-inflammatory effect in macrophage.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2024 Jun;46(3):319-329. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2024.2329621. Epub 2024 Mar 18. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2024. PMID: 38466121
Cited by
-
Osteocytes function as biomechanical signaling hubs bridging mechanical stress sensing and systemic adaptation.Front Physiol. 2025 Jul 15;16:1629273. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1629273. eCollection 2025. Front Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40735673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of plasma neuropeptide Y in acute myocardial infarction: a case-control study.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Nov 30;24(1):692. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-04373-1. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 39616326 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the Immunomodulatory and Neuroprotective Properties of Nigella sativa Oil in Experimental Systemic and Neuroinflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 2;26(5):2235. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052235. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076857 Free PMC article.
-
Novel insights into osteocyte and inter-organ/tissue crosstalk.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jan 17;14:1308408. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1308408. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38685911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuropeptide Y Peptide Family and Cancer: Antitumor Therapeutic Strategies.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 9;24(12):9962. doi: 10.3390/ijms24129962. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373115 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kellum JA, Romagnani P, Ashuntantang G, Ronco C, Zarbock A, Anders HJ. Acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7:52. - PubMed
-
- Neyra JA, Chawla LS. Acute Kidney Disease to Chronic Kidney Disease. Crit Care Clin. 2021;37:453–474. - PubMed
-
- Huang J, Xu D, Yang L. Acute Kidney Injury in Asia: Disease Burden. Semin Nephrol. 2020;40:443–455. - PubMed
-
- Jang HR, Rabb H. Immune cells in experimental acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2015;11:88–101. - PubMed
-
- Liu J. Dong Z. Neutrophil extracellular traps in ischemic AKI: new way to kill. Kidney Int. 2018;93:303–305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

