The role of STING signaling in central nervous system infection and neuroinflammatory disease
- PMID: 36632700
- PMCID: PMC10175194
- DOI: 10.1002/wsbm.1597
The role of STING signaling in central nervous system infection and neuroinflammatory disease
Abstract
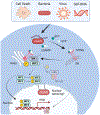
The cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate (GMP-AMP) synthase-Stimulator of Interferon Genes (cGAS-STING) pathway is a critical innate immune mechanism for detecting the presence of double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) and prompting a robust immune response. Canonical cGAS-STING activation occurs when cGAS, a predominantly cytosolic pattern recognition receptor, binds microbial DNA to promote STING activation. Upon STING activation, transcription factors enter the nucleus to cause the production of Type I interferons, inflammatory cytokines whose primary function is to prime the host for viral infection by producing a number of antiviral interferon-stimulated genes. While the pathway was originally described in viral infection, more recent studies have implicated cGAS-STING signaling in a number of different contexts, including autoimmune disease, cancer, injury, and neuroinflammatory disease. This review focuses on how our understanding of the cGAS-STING pathway has evolved over time with an emphasis on the role of STING-mediated neuroinflammation and infection in the nervous system. We discuss recent findings on how STING signaling contributes to the pathology of pain, traumatic brain injury, and stroke, as well as how mitochondrial DNA may promote STING activation in common neurodegenerative diseases. We conclude by commenting on the current knowledge gaps that should be filled before STING can be an effective therapeutic target in neuroinflammatory disease. This article is categorized under: Neurological Diseases > Molecular and Cellular Physiology Infectious Diseases > Molecular and Cellular Physiology Immune System Diseases > Molecular and Cellular Physiology.
Keywords: STING; brain injury; cGAS; interferons; neuroinflammation; stroke.
© 2023 The Authors. WIREs Mechanisms of Disease published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanism and therapeutic potential of targeting cGAS-STING signaling in neurological disorders.Mol Neurodegener. 2023 Nov 8;18(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s13024-023-00672-x. Mol Neurodegener. 2023. PMID: 37941028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of cGAS-STING signalling in liver diseases.JHEP Rep. 2021 Jun 24;3(5):100324. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2021.100324. eCollection 2021 Oct. JHEP Rep. 2021. PMID: 34381984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of cGAS-Sting Signaling in Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 2;24(9):8151. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098151. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The cGAS-STING Pathway in Bacterial Infection and Bacterial Immunity.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 13;12:814709. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.814709. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35095914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering and Delivery of cGAS-STING Immunomodulators for the Immunotherapy of Cancer and Autoimmune Diseases.Acc Chem Res. 2023 Nov 7;56(21):2933-2943. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.3c00394. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Acc Chem Res. 2023. PMID: 37802125 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Glia-Neurotrophic Factor Relationships: Possible Role in Pathobiology of Neuroinflammation-Related Brain Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 28;24(7):6321. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076321. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of microglia related neuroinflammation contributes to the protective effect of Gelsevirine on ischemic stroke.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 30;14:1164278. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1164278. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37063929 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotherapies in chronic pain through modulation of neuroimmune interactions.Pharmacol Ther. 2023 Aug;248:108476. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108476. Epub 2023 Jun 10. Pharmacol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37307899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Octadecanoids: Synthesis and Bioactivity of 18-Carbon Oxygenated Fatty Acids in Mammals, Bacteria, and Fungi.Chem Rev. 2025 Jan 8;125(1):1-90. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00520. Epub 2024 Dec 16. Chem Rev. 2025. PMID: 39680864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A central role of stimulator of interferon genes' adaptor protein in defensive immune response.Immunol Res. 2025 Jan 21;73(1):39. doi: 10.1007/s12026-024-09587-1. Immunol Res. 2025. PMID: 39836303 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

