Hearing loss in neonates and infants
- PMID: 36634668
- PMCID: PMC10475863
- DOI: 10.3345/cep.2022.01011
Hearing loss in neonates and infants
Abstract
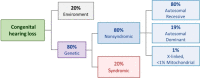
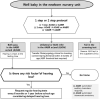
Hearing in neonates and infants is crucial for their development of language and communication skills. Unless hearing loss is appropriately managed early, it can cause a significant socioeconomic burden considering its detrimental impact on the child's development and its common nature. It is also the most common congenital sensory deficit, with an approximate incidence of 1.5 per 1,000 newborns. Its etiologies are heterogeneous: genetic causes are reportedly involved in up to 80% of cases, while congenital cytomegalovirus infection is the leading environmental factor contributing to congenital hearing loss. The introduction of newborn hearing screening using automated auditory brainstem response and/or automated otoacoustic emission in many developed countries has helped detect and manage hearing loss early. Current auditory rehabilitation options such as cochlear implantation implementing cutting-edge technologies can treat almost all degrees of hearing loss, emphasizing the importance of early hearing detection and intervention. Rapidly developing genetic diagnostic technologies and future cutting-edge treatment options, including gene therapy, will shed light on the future management of hearing loss in neonates and infants.
Keywords: Child development; Hearing loss; Infant; Newborn; State medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
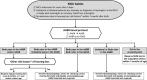

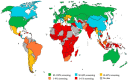

References
-
- Yoshinaga-Itano C, Sedey AL, Coulter DK, Mehl AL. Language of earlyand later-identified children with hearing loss. Pediatrics. 1998;102:1161–71. - PubMed
-
- Mohr PE, Feldman JJ, Dunbar JL, McConkey-Robbins A, Niparko JK, Rittenhouse RK, et al. The societal costs of severe to profound hearing loss in the United States. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 2000;16:1120–35. - PubMed
-
- American Academy of Pediatrics. Joint Committee on Infant Hearing Year 2007 position statement: principles and guidelines for early hearing detection and intervention programs. Pediatrics. 2007;120:898–921. - PubMed
-
- The Joint Committee on Infant Hearing Year 2019 position statement: principles and guidelines for early hearing detection and intervention programs. J Early Hear Detect Interv. 2019;4:1–44.
-
- Thompson DC, McPhillips H, Davis RL, Lieu TL, Homer CJ, Helfand M. Universal newborn hearing screening: summary of evidence. JAMA. 2001;286:2000–10. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources