Integrator is a global promoter-proximal termination complex
- PMID: 36634676
- PMCID: PMC10866050
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.11.012
Integrator is a global promoter-proximal termination complex
Abstract
Integrator is a metazoan-specific protein complex capable of inducing termination at all RNAPII-transcribed loci. Integrator recognizes paused, promoter-proximal RNAPII and drives premature termination using dual enzymatic activities: an endonuclease that cleaves nascent RNA and a protein phosphatase that removes stimulatory phosphorylation associated with RNAPII pause release and productive elongation. Recent breakthroughs in structural biology have revealed the overall architecture of Integrator and provided insights into how multiple Integrator modules are coordinated to elicit termination effectively. Furthermore, functional genomics and biochemical studies have unraveled how Integrator-mediated termination impacts protein-coding and noncoding loci. Here, we review the current knowledge about the assembly and activity of Integrator and describe the role of Integrator in gene regulation, highlighting the importance of this complex for human health.
Keywords: Integrator; attenuation; elongation control; gene regulation; polymerase pausing; transcription termination.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests K.A. is on the SAB of CAMP4 Therapeutics, received research funding from Novartis, and is a member of the advisory board of Molecular Cell.
Figures
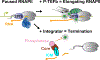


References
-
- Fujinaga K, Irwin D, Huang Y, Taube R, Kurosu T, and Peterlin BM (2004). Dynamics of human immunodeficiency virus transcription: P-TEFb phosphorylates RD and dissociates negative effectors from the transactivation response element. Mol Cell Biol 24, 787–795. 10.1128/MCB.24.2.787-795.2004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

