Assembly chaperone Nas6 selectively destabilizes 26S proteasomes with defective regulatory particle-core particle interfaces
- PMID: 36634850
- PMCID: PMC9943895
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.102894
Assembly chaperone Nas6 selectively destabilizes 26S proteasomes with defective regulatory particle-core particle interfaces
Abstract
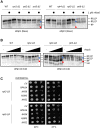
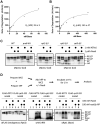
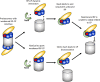
The 26S proteasome is a 66-subunit-chambered protease present in all eukaryotes that maintains organismal health by degrading unneeded or defective proteins. Defects in proteasome function or assembly are known to contribute to the development of various cancers, neurodegeneration, and diabetes. During proteasome biogenesis, a family of evolutionarily conserved chaperones assembles a hexameric ring of AAA+ family ATPase subunits contained within the proteasomal regulatory particle (RP) and guide their docking onto the surface of the proteolytic core particle (CP). This RP-CP interaction couples the substrate capture and unfolding process to proteolysis. We previously reported a mutation in the proteasome that promoted dissociation of the RP and CP by one of these chaperones, Nas6. However, the nature of the signal for Nas6-dependent proteasome disassembly and the generality of this postassembly proteasome quality control function for Nas6 remain unknown. Here, we use structure-guided mutagenesis and in vitro proteasome disassembly assays to demonstrate that Nas6 more broadly destabilizes 26S proteasomes with a defective RP-CP interface. We show that Nas6 can promote dissociation of mature proteasomes into RP and CP in cells harboring defects on either side of the RP-CP interface. This function is unique to Nas6 and independent from other known RP assembly chaperones. Further biochemical experiments suggest that Nas6 may exploit a weakened RP-CP interface to dissociate the RP from the CP. We propose that this postassembly role of Nas6 may fulfill a quality control function in cells by promoting the recycling of functional subcomplexes contained within defective proteasomes.
Keywords: 26S proteasome; assembly; chaperone; macromolecular complex; proteolysis; quality control; ubiquitin.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures




References
-
- Rousseau A., Bertolotti A. Regulation of proteasome assembly and activity in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018;19:697–712. - PubMed
-
- Groll M., Huber R. Substrate access and processing by the 20S proteasome core particle. Int. J. Biochem. Cel. Biol. 2003;35:606–616. - PubMed
-
- Jäger S., Groll M., Huber R., Wolf D.H., Heinemeyer W. Proteasome beta-type subunits: unequal roles of propeptides in core particle maturation and a hierarchy of active site function. J. Mol. Biol. 1999;291:997–1013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

