The Link between Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Sarcopenia: An Update Focusing on the Role of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase 4
- PMID: 36635027
- PMCID: PMC10040620
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0305
The Link between Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Sarcopenia: An Update Focusing on the Role of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase 4
Abstract
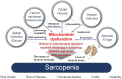
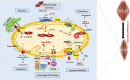
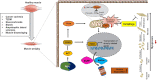
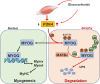
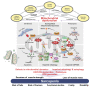
Sarcopenia, defined as a progressive loss of muscle mass and function, is typified by mitochondrial dysfunction and loss of mitochondrial resilience. Sarcopenia is associated not only with aging, but also with various metabolic diseases characterized by mitochondrial dyshomeostasis. Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinases (PDKs) are mitochondrial enzymes that inhibit the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, which controls pyruvate entry into the tricarboxylic acid cycle and the subsequent adenosine triphosphate production required for normal cellular activities. PDK4 is upregulated in mitochondrial dysfunction-related metabolic diseases, especially pathologic muscle conditions associated with enhanced muscle proteolysis and aberrant myogenesis. Increases in PDK4 are associated with perturbation of mitochondria-associated membranes and mitochondrial quality control, which are emerging as a central mechanism in the pathogenesis of metabolic disease-associated muscle atrophy. Here, we review how mitochondrial dysfunction affects sarcopenia, focusing on the role of PDK4 in mitochondrial homeostasis. We discuss the molecular mechanisms underlying the effects of PDK4 on mitochondrial dysfunction in sarcopenia and show that targeting mitochondria could be a therapeutic target for treating sarcopenia.
Keywords: Metabolic diseases; Mitochondria; Muscular atrophy; Pyruvate dehydrogenase acetyl-transferring kinase; Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex; Sarcopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Shimokata H, Shimada H, Satake S, Endo N, Shibasaki K, Ogawa S, et al. Chapter 2 Epidemiology of sarcopenia. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2018;18 Suppl 1:13–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

