Closer view of antennal sensory organs of two Leptoglossus species (Insecta, Hemiptera, Coreidae)
- PMID: 36635483
- PMCID: PMC9837090
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-27837-4
Closer view of antennal sensory organs of two Leptoglossus species (Insecta, Hemiptera, Coreidae)
Abstract
Detailed description of antennal sensory organs of Leptoglossus occidentalis Heidemann, 1910 (Insecta: Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Coreidae) and a comparison with L. zonatus (Dallas, 1852) are presented. A novel approach that combines the advantages of field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) and atomic force microscope (AFM) was used to detail micromorphological structures. A simplified classification system for sensilla that eliminates the subjective aspects of morphology, such as their shape, is proposed. Fourteen sensory organs have been classified into three main groups: (a) aporous sensilla with a flexible socket, (b) porous sensilla with a flexible socket and (c) porous sensilla with an inflexible socket. A large variety of sensory organs (nine types) with olfactory functions are described. The antennal sensory organs have been recognized as one of the factors responsible for the evolutionary success of Leptoglossus spp. and their status as important pests and invasive species.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





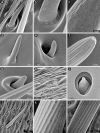


References
-
- Henry TJ. Biodiversity of heteroptera. In: Foottit RG, Adler PH, editors. Insect Biodiversity: Science and Society. Wiley; 2017. pp. 279–335.
-
- Schuh, R. T. & Weirauch, C. True Bugs of the World (Hemiptera: Heteroptera): Classification and Natural History, 2nd ed. Siri Scientific Press Monograph Series, vol. 8, (2020).
-
- Guérin-Méneville, F. É. 2 Crustaces, Arachnides et Insectes. In Voyage autour du monde, exécuté par ordre du Roi, sur la corvette de Sa Majesté "La Coquille", pendant les années 1822–1825 (ed. Duperrey, L. I.) Zoologie Bertrand, Paris. i-xii, 1–319 (1831).
-
- Leston D, Pendergrast JG, Southwood TRE. Classification of the terrestrial Heteroptera (Geocorisae) Nature. 1954;174(4419):91–92. doi: 10.1038/174091b0. - DOI
-
- Leach WE. Entomology. In: Brewster D, editor. The Edinburgh Encyclopaedia. Blackwood; 1815. pp. 57–172.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

