Multiplexed screens identify RAS paralogues HRAS and NRAS as suppressors of KRAS-driven lung cancer growth
- PMID: 36635501
- PMCID: PMC10521195
- DOI: 10.1038/s41556-022-01049-w
Multiplexed screens identify RAS paralogues HRAS and NRAS as suppressors of KRAS-driven lung cancer growth
Abstract
Oncogenic KRAS mutations occur in approximately 30% of lung adenocarcinoma. Despite several decades of effort, oncogenic KRAS-driven lung cancer remains difficult to treat, and our understanding of the regulators of RAS signalling is incomplete. Here to uncover the impact of diverse KRAS-interacting proteins on lung cancer growth, we combined multiplexed somatic CRISPR/Cas9-based genome editing in genetically engineered mouse models with tumour barcoding and high-throughput barcode sequencing. Through a series of CRISPR/Cas9 screens in autochthonous lung cancer models, we show that HRAS and NRAS are suppressors of KRASG12D-driven tumour growth in vivo and confirm these effects in oncogenic KRAS-driven human lung cancer cell lines. Mechanistically, RAS paralogues interact with oncogenic KRAS, suppress KRAS-KRAS interactions, and reduce downstream ERK signalling. Furthermore, HRAS and NRAS mutations identified in oncogenic KRAS-driven human tumours partially abolished this effect. By comparing the tumour-suppressive effects of HRAS and NRAS in oncogenic KRAS- and oncogenic BRAF-driven lung cancer models, we confirm that RAS paralogues are specific suppressors of KRAS-driven lung cancer in vivo. Our study outlines a technological avenue to uncover positive and negative regulators of oncogenic KRAS-driven cancer in a multiplexed manner in vivo and highlights the role RAS paralogue imbalance in oncogenic KRAS-driven lung cancer.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS STATEMENT
M.M.W. and D.A.P are co-founders of, and hold equity in, D2G Oncology, Inc.
The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


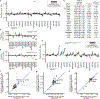

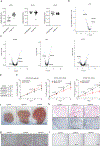
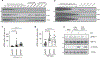


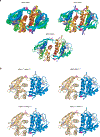



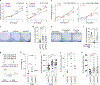


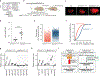
References
-
- Wennerberg K, Rossman KL & Der CJ The Ras superfamily at a glance. Journal of cell science 118, 843–846 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA231253/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA230025/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM118165/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA234349/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA197687/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 CA256039/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F30 GM142263/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R00 CA256039/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM122517/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA250534/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA124435/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA006927/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

