Targeting Menin disrupts the KMT2A/B and polycomb balance to paradoxically activate bivalent genes
- PMID: 36635503
- PMCID: PMC7614190
- DOI: 10.1038/s41556-022-01056-x
Targeting Menin disrupts the KMT2A/B and polycomb balance to paradoxically activate bivalent genes
Abstract
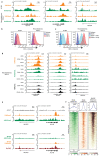
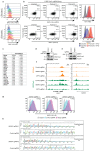
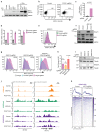
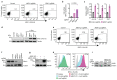
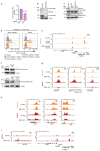
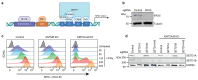
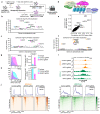
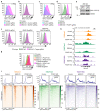
Precise control of activating H3K4me3 and repressive H3K27me3 histone modifications at bivalent promoters is essential for normal development and frequently corrupted in cancer. By coupling a cell surface readout of bivalent MHC class I gene expression with whole-genome CRISPR-Cas9 screens, we identify specific roles for MTF2-PRC2.1, PCGF1-PRC1.1 and Menin-KMT2A/B complexes in maintaining bivalency. Genetic loss or pharmacological inhibition of Menin unexpectedly phenocopies the effects of polycomb disruption, resulting in derepression of bivalent genes in both cancer cells and pluripotent stem cells. While Menin and KMT2A/B contribute to H3K4me3 at active genes, a separate Menin-independent function of KMT2A/B maintains H3K4me3 and opposes polycomb-mediated repression at bivalent genes. Release of KMT2A from active genes following Menin targeting alters the balance of polycomb and KMT2A at bivalent genes, facilitating gene activation. This functional partitioning of Menin-KMT2A/B complex components reveals therapeutic opportunities that can be leveraged through inhibition of Menin.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
M.A.D. has been a member of advisory boards for GSK, CTX CRC, Storm Therapeutics, Celgene and Cambridge Epigenetix. The Dawson Laboratory is a recipient of grant funding through the emerging science fund administered through Pfizer. S.J.D. has been a member of advisory boards for Adela and Inivata. P.E. owns Amgen stocks (less than 5% value of company) and has undertaken prior consulting for Servier (less than $10,000). G.M.M is employed by Syndax Pharmaceuticals. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
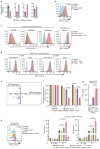
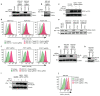
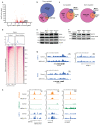
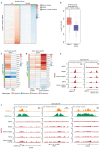
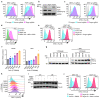
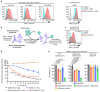
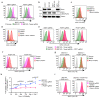

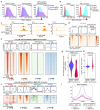
Comment in
-
Dissecting MENIN in bivalent gene regulation.Nat Cell Biol. 2023 Feb;25(2):209-210. doi: 10.1038/s41556-022-01063-y. Nat Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 36635502 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cenik BK, Shilatifard A. COMPASS and SWI/SNF complexes in development and disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2021;22:38–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 086615/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 210688/Z/18/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 085733/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 102157/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 089957/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 102163/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 091181/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 20097/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 084957/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 210688/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- C53779/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 051269/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 060324/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 204845/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MR/R001405/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 101835/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 101835/Z/13/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 204017/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MR/V011561/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0600823/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- A20097/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

