Serum miR-342-3p Acts as a Biomarker for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Participates in the Disease Progression
- PMID: 36636634
- PMCID: PMC9829984
- DOI: 10.2147/CCID.S378985
Serum miR-342-3p Acts as a Biomarker for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Participates in the Disease Progression
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of this study was to investigate the diagnostic ability and prognostic value of miR-342-3p in SLE patients by detecting the expression level of serum miR-342-3p in SLE patients.
Patients and methods: The expression level of serum miR-342-3p in all subjects was determined by qRT-PCR technology, and the correlation of miR-342-3p with SLEDAI scores was evaluated using Spearman correlation coefficient. The diagnostic value of miR-342-3p in SLE was assessed using ROC curve. The prognostic value of miR-342-3p in SLE patients was analyzed by Kaplan-Meier survival curve and multivariate COX regression.
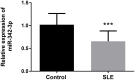
Results: The qRT-PCR results showed that the expression level of serum miR-342-3p in SLE patients was significantly lower than that in healthy controls (P < 0.001). Serum miR-342-3p expression level was negatively correlated with SLEDAI scores (r = - 0.810, P < 0.001). The ROC curve suggested that serum miR-342-3p expression level was discriminative between SLE patients and healthy controls. Survival analysis results indicated that SLE patients with low serum miR-342-3p expression had a higher probability of poor prognosis of SLE (Log rank P = 0.003).
Conclusion: The expression level of serum miR-342-3p was valuable in the diagnosis of SLE. Meanwhile, the low expression level of serum miR-342-3p was associated with the poor prognosis of SLE.
Keywords: diagnosis; miR-342-3p; prognosis; systemic lupus erythematosus.
© 2023 You et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

