Impact of Hemin on Interleukin-21 Levels and Plasma Cells in Transfusion-Dependent Thalassemia with Positive and Negative Allo-Autoantibody
- PMID: 36636711
- PMCID: PMC9830417
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S397317
Impact of Hemin on Interleukin-21 Levels and Plasma Cells in Transfusion-Dependent Thalassemia with Positive and Negative Allo-Autoantibody
Abstract
Introduction: Antibody formation in transfusion-dependent thalassemia is associated with chronic hemolysis and repeated transfusions. Hemolysis produces heme, which mediates B-cell differentiation into plasma cells and produces antibodies influenced by interleukin-21 (IL-21).
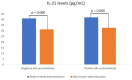
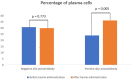
Objective: This study aimed to compare IL-21 levels, plasma cell percentage, and red blood cell antibodies between positive and negative allo-autoantibody thalassemia before and after hemin administration.
Materials and methods: This research employed a quasi-experimental nonequivalent control group pre-test and post-test design performed from April to November 2021 at Soetomo Academic Hospital in Surabaya, Indonesia. Heparinized blood samples of 5 mL and 4 mL and EDTA blood samples of 3 mL were taken from positive (29 patients) and negative (28 patients) allo-autoantibody thalassemia participants. Hemin 20 µM was added to 5 mL of heparinized blood, incubated for 2 hours, prepared into peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), and cultured for 3 days. The percentage of plasma cells (CD38+CD184+) of cultured and uncultured PBMCs was measured by BD FACSCalibur Flow Cytometer. IL-21 levels of plasma and supernatants were measured with Sandwich Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay by Elabscience. Red blood cell antibodies were detected by QWALYS 3 E.M. Technology. Autoantibodies were determined by the Grifols gel tube method.
Results: IL-21 levels were significantly different in the positive and negative allo-autoantibody thalassemia groups after hemin administration. The percentage of plasma cells in the positive allo-autoantibody group increased significantly after the administration of hemin. The percentage of plasma cells between thalassemia groups was not significantly different before the hemin administration but increased significantly after it. Red blood cell antibodies after the administration of hemin were significantly different in the negative allo-autoantibody group but not significantly different in the positive allo-autoantibody group.
Conclusion: Hemin administration affected IL-21 levels, plasma cell percentage, and antibody formation in positive and negative allo-auto antibody thalassemia.
Keywords: IL-21 levels; plasma cells; red blood cells antibody; thalassemia disease.
© 2023 Tambunan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced the work reported in this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of Hemin in the Immune Response of T Follicular Helper Lymphocytes Expressing T-Cell Immunoreceptor with Immunoglobulin and Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-Based Inhibitory Domains, Programmed Cell Death-1, and Interleukin-21 in Allo-Auto Positive and Negative Thalassemia.J Blood Med. 2023 Jan 13;14:7-17. doi: 10.2147/JBM.S393134. eCollection 2023. J Blood Med. 2023. PMID: 36660451 Free PMC article.
-
Frequency of red cell allo- and autoimmunization in patients with transfusion-dependent beta thalassemia and affecting factors.Turk J Pediatr. 2014 Sep-Oct;56(5):487-92. Turk J Pediatr. 2014. PMID: 26022583
-
Red blood cells alloimmunization and autoimmunization among transfusion-dependent beta-thalassemia patients in Alexandria province, Egypt.Transfus Apher Sci. 2015 Aug;53(1):52-7. doi: 10.1016/j.transci.2015.03.006. Epub 2015 Mar 12. Transfus Apher Sci. 2015. PMID: 25817267 Clinical Trial.
-
Red Blood Cell Antigen Genotyping for Sickle Cell Disease, Thalassemia, and Other Transfusion Complications.Transfus Med Rev. 2016 Oct;30(4):197-201. doi: 10.1016/j.tmrv.2016.05.011. Epub 2016 May 28. Transfus Med Rev. 2016. PMID: 27345938 Review.
-
Red cell alloimmunization in transfusion-dependent and transfusion-independent beta thalassemia: A review from the Eastern Mediterranean Region (EMRO).Transfus Apher Sci. 2019 Dec;58(6):102678. doi: 10.1016/j.transci.2019.102678. Epub 2019 Nov 7. Transfus Apher Sci. 2019. PMID: 31753776 Review.
References
-
- Wahidiyat PA, Sari TT, Rahmartani LD, et al. An insight into Indonesian current thalassaemia care and challenges. ISBT Sci Ser. 2020;2020:1–8.
-
- Jazuli MI, Bintoro SUY, Mudjanarko SW. The association between serum ferritin levels and 25 (OH) D levels in adult patients with transfusion dependent thalassemia. J Med Chem Sci. 2022;5:35–41.
-
- Fonda T, Novida H. Management of gestational diabetes mellitus in a beta major thalassemia patient. Curr Intern Med Res Pract Surabaya J. 2021;2:45. doi:10.20473/cimrj.v2i2.26255 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous