Binary Nanodrug-Delivery System Designed for Leukemia Therapy: Aptamer- and Transferrin-Codecorated Daunorubicin- and Luteolin-Coloaded Nanoparticles
- PMID: 36636745
- PMCID: PMC9830956
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S387246
Binary Nanodrug-Delivery System Designed for Leukemia Therapy: Aptamer- and Transferrin-Codecorated Daunorubicin- and Luteolin-Coloaded Nanoparticles
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to develop a binary nanodrug-delivery system decorated with aptamers (APs) and transferrin (Tf) and loaded with daunorubicin (Drn) and luteolin (Lut) for the treatment of leukemia.
Methods: Oligonucleotide AP- and Tf-contaiing ligands were designed and synthesized separately. AP-decorated Drn-loaded nanoparticles (AP-Drn NPs) and Tf-Lut NPs were prepared by self-assembly. An AP- and Tf-codecorated Drn- and Lut-coloaded nanodrug-delivery system (AP/Tf-Drn/Lut NPs) was prepared by self-assembly of AP-Drn NPs and Tf-Lut NPs. In vitro and in vivo efficiency of the system was evaluated on leukemia cell line and cell-bearing mouse model in comparison with single ligand-decorated, single drug-loaded and free-drug formulations.
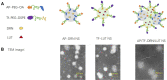
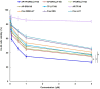
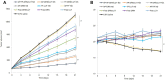
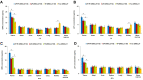
Results: AP/Tf-Drn/Lut NPs were spherical and nanosized (187.3±5.3 nm) and loaded with about 85% of drugs. In vitro cytotoxicity of AP/Tf-Drn/Lut NPs was remarkably higher than single ligand-decorated ones. Double drug-loaded AP/Tf-Drn/Lut NPs exhibited higher tumor-cell inhibition than single drug-loaded ones, which showed a synergic effect of the two drugs. AP/Tf-Drn/Lut NPs achieved the most efficient antileukemic activity and absence of toxicity in vivo.
Conclusion: The present study showed that AP/Tf-Drn/Lut NPs are a promising drug-delivery system for targeted treatment of leukemia, due to the synergic effect of the two drugs in this system. The limitations of this system include stability during large-scale production and application from bench to bedside.
Keywords: acute myeloid leukemia; aptamer; daunorubicin; luteolin; nanodrug-delivery system; transferrin.
© 2023 Zhu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Applications of daunorubicin-loaded PLGA-PLL-PEG-Tf nanoparticles in hematologic malignancies: an in vitro and in vivo evaluation.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Apr 8;13:1107-1115. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S195832. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31040647 Free PMC article.
-
PLGA-PLL-PEG-Tf-based targeted nanoparticles drug delivery system enhance antitumor efficacy via intrinsic apoptosis pathway.Int J Nanomedicine. 2015 Jan 12;10:557-66. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S75090. eCollection 2015. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015. PMID: 25609961 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin-Loaded Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Melanoma.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Apr 20;18:2053-2068. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S400329. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37101838 Free PMC article.
-
The Recent Development of Luteolin-loaded Nanocarrier in Targeting Cancer.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(27):2129-2141. doi: 10.2174/0113816128313713240628063301. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 38963114 Review.
-
Nanoparticles loaded with Daunorubicin as an advanced tool for cancer therapy.Eur J Med Chem. 2023 Oct 5;258:115547. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115547. Epub 2023 Jun 5. Eur J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37327678 Review.
Cited by
-
Flavonoids as Chemosensitizers in Leukemias.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025;1479:205-234. doi: 10.1007/5584_2024_828. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 39503945 Review.
-
4-Deoxy-ε-Pyrromycinone: A Promising Drug/Lead Compound to Treat Tumors.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Jun 18;18:2367-2379. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S461594. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 38911033 Free PMC article.
-
Aptamers for the Delivery of Plant-Based Compounds: A Review.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Apr 14;16(4):541. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16040541. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38675202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aptamers Versus Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF): A New Battle against Ovarian Cancer.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Jun 6;16(6):849. doi: 10.3390/ph16060849. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37375796 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

