Neural representations of the perception of handwritten digits and visual objects from a convolutional neural network compared to humans
- PMID: 36637109
- PMCID: PMC9980894
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.26189
Neural representations of the perception of handwritten digits and visual objects from a convolutional neural network compared to humans
Abstract
We investigated neural representations for visual perception of 10 handwritten digits and six visual objects from a convolutional neural network (CNN) and humans using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). Once our CNN model was fine-tuned using a pre-trained VGG16 model to recognize the visual stimuli from the digit and object categories, representational similarity analysis (RSA) was conducted using neural activations from fMRI and feature representations from the CNN model across all 16 classes. The encoded neural representation of the CNN model exhibited the hierarchical topography mapping of the human visual system. The feature representations in the lower convolutional (Conv) layers showed greater similarity with the neural representations in the early visual areas and parietal cortices, including the posterior cingulate cortex. The feature representations in the higher Conv layers were encoded in the higher-order visual areas, including the ventral/medial/dorsal stream and middle temporal complex. The neural representations in the classification layers were observed mainly in the ventral stream visual cortex (including the inferior temporal cortex), superior parietal cortex, and prefrontal cortex. There was a surprising similarity between the neural representations from the CNN model and the neural representations for human visual perception in the context of the perception of digits versus objects, particularly in the primary visual and associated areas. This study also illustrates the uniqueness of human visual perception. Unlike the CNN model, the neural representation of digits and objects for humans is more widely distributed across the whole brain, including the frontal and temporal areas.
Keywords: convolutional neural network; functional magnetic resonance imaging; handwritten digits; representational similarity analysis; visual objects; visual perception.
© 2023 The Authors. Human Brain Mapping published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest regarding this study, including financial, consultant, institutional, or other relationships. The sponsor was not involved in the study design, data collection, analysis or interpretation of the data, manuscript preparation, or the decision to submit for publication.
Figures





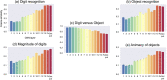

References
-
- Ansari, D. , Lyons, I. M. , van Eimeren, L. , & Xu, F. (2007). Linking visual attention and number processing in the brain: The role of the temporo‐parietal junction in small and large symbolic and nonsymbolic number comparison. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 19(11), 1845–1853. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

