Habitual exercise influences carotid artery strain and strain rate, but not cognitive function in healthy middle-aged females
- PMID: 36637510
- PMCID: PMC10119229
- DOI: 10.1007/s00421-022-05123-x
Habitual exercise influences carotid artery strain and strain rate, but not cognitive function in healthy middle-aged females
Abstract
Purpose: Aging females are at risk of declining vascular and cognitive function. Exercise can augment both factors independently; however, the influence of exercise on their interdependence is less clearly understood. Ultrasound speckle tracking is a sensitive novel measure of arterial aging but has not previously been used in middle-aged females. We aimed to elucidate the potential interactions between vascular and cognitive variables in active aging females.
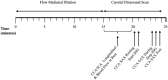
Methods: Twelve active (56 ± 5 years; [Formula: see text]: 34.5 ± 6.1 ml.kg.min-1) and 13 inactive (57 ± 4 years; 22.8 ± 2.6 ml.kg.min-1) healthy middle-aged females were included. Ultrasound speckle tracking assessed short-axis common carotid artery (CCA) compliance via peak circumferential strain (PCS) and strain rate (PSR) at rest, during, and after 3-min isometric handgrip exercise. Flow-mediated dilation (FMD) of the brachial artery was assessed using ultrasound. Cognitive function was measured using Verbal Fluency, Trail Making, Stroop, and Digit Span tests.
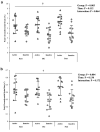
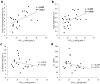
Results: PCS (P = 0.003) and PSR (P = 0.004), were higher in the active cohort. FMD was similar between groups (P > 0.05). Minimal differences in cognitive function existed between groups, although the inactive group performed better in one test of animal Verbal Fluency (P < 0.01). No associations were observed between PCS, PSR, or FMD with cognitive function (all P > 0.05).
Conclusion: This is the first study to assess PCS and PSR in middle-aged females and demonstrates that active middle-aged females exhibit a superior carotid artery profile compared to their inactive counterparts. However, PCS and PSR of the carotid artery may not be linked with cognitive function in middle-aged females.
Keywords: Aging; Carotid function; Cognitive function; Exercise; Flow-mediated dilation; Speckle tracking.
© 2023. Crown.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare. No funding was received for conducting this study.
Figures
References
-
- Aichberger M, Busch M, Reischies F, et al. Effect of physical inactivity on cognitive performance after 2.5 years of follow-up: longitudinal results from the survey of health, ageing, and retirement (SHARE) J Gerontopsychology Geriatr Psychiatry. 2010;23:7–15. doi: 10.1024/1662-9647/a000003. - DOI
-
- Azhim A, Akioka K, Akutagawa M, et al (2007) Effects of aging and exercise training on the common carotid blood velocities in healthy men. In: 2007 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. IEEE, Lyon, France, pp 989–993 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

