CD19 Is Internalized Together with IgM in Proportion to B Cell Receptor Stimulation and Is Modulated by Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase in Bone Marrow Immature B Cells
- PMID: 36637517
- PMCID: PMC10074640
- DOI: 10.4049/immunohorizons.2200092
CD19 Is Internalized Together with IgM in Proportion to B Cell Receptor Stimulation and Is Modulated by Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase in Bone Marrow Immature B Cells
Abstract
Newly generated immature B cells that bind self-antigen with high avidity arrest in differentiation and undergo central tolerance via receptor editing and clonal deletion. These autoreactive immature B cells also express low surface levels of the coreceptor CD19, a key activator of the PI3K pathway. Signals emanating from both CD19 and PI3K are known to be critical for attenuating receptor editing and selecting immature B cells into the periphery. However, the mechanisms that modulate CD19 expression at this stage of B cell development have not yet been resolved. Using in vivo and in vitro models, we demonstrate that Cd19 de novo gene transcription and translation do not significantly contribute to the differences in CD19 surface expression in mouse autoreactive and nonautoreactive immature B cells. Instead, CD19 downregulation is induced by BCR stimulation in proportion to BCR engagement, and the remaining surface IgM and CD19 molecules promote intracellular PI3K-AKT activity in proportion to their level of expression. The internalized CD19 is degraded with IgM by the lysosome, but inhibiting lysosome-mediated protein degradation only slightly improves surface CD19. In fact, CD19 is restored only upon Ag removal. Our data also reveal that the PI3K-AKT pathway positively modulates CD19 surface expression in immature B cells via a mechanism that is independent of inhibition of FOXO1 and its role on Cd19 gene transcription while is dependent on mTORC1.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures




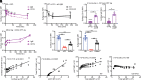
![FIGURE 6. PI3K signaling positively modulates surface CD19 in immature B cells via the AKT-mTORC1 axis. (A) Relative surface CD19 and IgM levels on ex vivo B220+CD24highCD23− immature B cells from 3-83Igi,H-2b autoreactive (AUT) mice that did or did not express the active PI3Kα form P110*. Data (mean ± SD; n = 5 mice analyzed in four independent experiments) are expressed as fold change over ex vivo immature B cells from 3-83Igi,H-2d nonautoreactive (NA) mice, represented by a blue dashed line. The p values were calculated using one-sample t test and are displayed above each bar, whereas differences between bars were calculated using an unpaired t test displayed on top of horizontal lines. (B) Relative surface CD19 and IgM measured on NA and NA-P110* B220+CD24highCD23− immature B cells that were cultured for 20 h on a Kb stromal cell layer. Data (mean ± SD; n = 3 mice analyzed in three independent experiments) are expressed as fold change over NA immature B cells cultured on Kd stromal. The p values were calculated using an unpaired t test. (C and D) Relative surface CD19 and IgM on B220+CD24highCD23− immature B cells from indicated mice that were cultured for 20 h with inhibitors for ERK (FR180204, 30 μM), AKT (afuresertib, 5 μM), or mTORC1 (rapamycin, 10 μM) and relative to cells treated with DMSO control. Data [mean ± SD; 5 mice/group from five experiments in (C) and 4 mice/group from two experiments in (D)] are expressed as fold change over NA immature B cells cultured with DMSO. The p values denoting differences from NA plus DMSO samples were calculated using a one-sample t test and are placed above each bar. Differences between bars were calculated with a t test and are displayed above horizontal lines. Relative surface CD19 on ex vivo B220+CD24highCD23− immature B cells from 3-83Igi,H-2b AUT mice (E) in which B cells express or not the active PI3Kα P110* or carry the deletion of FOXO1 or from 3-83Igi,H-2d NA mice (F) in which B cells express or not the constitutively active FOXO1-AAA. Data [mean ± SD; 6 mice/group from five experiments in (E) and 5 mice/group from three experiments in (F)] are expressed as fold change over AUT immature B cells in (E) or fold change over NA immature B cells in (F). The p values were calculated using a one-sample t test and displayed above each bar. Differences between bars in (E) were calculated with an unpaired t test. (G) Relative surface CD19 on NA B220+CD24highCD23− immature B cells cultured for 20 h with inhibitors for transcription (actinomycin D [ActD], 0.1 μM) or AKT (afuresertib, 5 μM). Data (mean ± SD; n = 4 mice/group from two experiments) are expressed as fold change over NA treated with DMSO. The p values were calculated using a one-sample t test and displayed above each graph or a paired t test displayed above a horizontal line. In all bar graphs, *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001.](https://cdn.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/blobs/4613/10563398/f60c2a9700cf/ih2200092f6.gif)
References
-
- Wardemann H., Yurasov S., Schaefer A., Young J. W., Meffre E., Nussenzweig M. C.. 2003. Predominant autoantibody production by early human B cell precursors. Science 301: 1374–1377. - PubMed
-
- Grandien A., Fucs R., Nobrega A., Andersson J., Coutinho A.. 1994. Negative selection of multireactive B cell clones in normal adult mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 24: 1345–1352. - PubMed
-
- Nemazee D. 2006. Receptor editing in lymphocyte development and central tolerance. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6: 728–740. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

