Toward naturalistic neuroscience: Mechanisms underlying the flattening of brain hierarchy in movie-watching compared to rest and task
- PMID: 36638163
- PMCID: PMC9839335
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ade6049
Toward naturalistic neuroscience: Mechanisms underlying the flattening of brain hierarchy in movie-watching compared to rest and task
Abstract
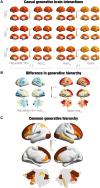
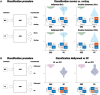
Identifying the functional specialization of the brain has moved from using cognitive tasks and resting state to using ecological relevant, naturalistic movies. We leveraged a large-scale neuroimaging dataset to directly investigate the hierarchical reorganization of functional brain activity when watching naturalistic films compared to performing seven cognitive tasks and resting. A thermodynamics-inspired whole-brain model paradigm revealed the generative underlying mechanisms for changing the balance in causal interactions between brain regions in different conditions. Paradoxically, the hierarchy is flatter for movie-watching, and the level of nonreversibility is significantly smaller in comparison to both rest and tasks, where the latter in turn have the highest levels of hierarchy and nonreversibility. The underlying mechanisms were revealed by the model-based generative effective connectivity (GEC). Naturalistic films could therefore provide a fast and convenient way to measure important changes in GEC (integrating functional and anatomical connectivity) found in, for example, neuropsychiatric disorders. Overall, this study demonstrates the benefits of moving toward a more naturalistic neuroscience.
Figures

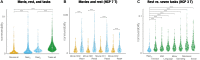

References
-
- S. Sonkusare, M. Breakspear, C. Guo, Naturalistic stimuli in neuroscience: Critically acclaimed. Trends Cogn. Sci. 23, 699–714 (2019). - PubMed
-
- U. Hasson, Y. Nir, I. Levy, G. Fuhrmann, R. Malach, Intersubject synchronization of cortical activity during natural vision. Science 303, 1634–1640 (2004). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

