LncRNA LIMp27 Regulates the DNA Damage Response through p27 in p53-Defective Cancer Cells
- PMID: 36638271
- PMCID: PMC9982580
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202204599
LncRNA LIMp27 Regulates the DNA Damage Response through p27 in p53-Defective Cancer Cells
Erratum in
-
Correction to "LncRNA LIMp27 Regulates the DNA Damage Response Through p27 in p53-Defective Cancer Cells".Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Mar;12(10):e2500857. doi: 10.1002/advs.202500857. Epub 2025 Jan 30. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39887583 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
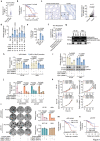
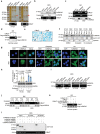
P53 inactivation occurs in about 50% of human cancers, where p53-driven p21 activity is devoid and p27 becomes essential for the establishment of the G1/S checkpoint upon DNA damage. Here, this work shows that the E2F1-responsive lncRNA LIMp27 selectively represses p27 expression and contributes to proliferation, tumorigenicity, and treatment resistance in p53-defective colon adenocarcinoma (COAD) cells. LIMp27 competes with p27 mRNA for binding to cytoplasmically localized hnRNA0, which otherwise stabilizes p27 mRNA leading to cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 phase. In response to DNA damage, LIMp27 is upregulated in both wild-type and p53-mutant COAD cells, whereas cytoplasmic hnRNPA0 is only increased in p53-mutant COAD cells due to translocation from the nucleus. Moreover, high LIMp27 expression is associated with poor survival of p53-mutant but not wild-type p53 COAD patients. These results uncover an lncRNA mechanism that promotes p53-defective cancer pathogenesis and suggest that LIMp27 may constitute a target for the treatment of such cancers.
Keywords: E2F1; LIMp27; colon cancer; hnRNPA0; lncRNA; p27.
© 2023 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82 002 571/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- U2004138/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82 002 442/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82 173 138/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 21 230 040 016/Excellent Youth Foundation of He'nan Scientific Committee
- RG20-01/China; Hunter Medical Research Institute (T. La), Australia; the Cancer Council NSW
- RG21-10/China; Hunter Medical Research Institute (T. La), Australia; the Cancer Council NSW
- 1 162 753/Australia; the National Health and Medical Research Council
- 1 177 087/Australia; the National Health and Medical Research Council
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
