Patients with Asian-type DEL can safely be transfused with RhD-positive blood
- PMID: 36638337
- PMCID: PMC10273079
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2022018152
Patients with Asian-type DEL can safely be transfused with RhD-positive blood
Abstract
Red blood cells (RBCs) of Asian-type DEL phenotype express few RhD proteins and are typed as serologic RhD-negative (D-) phenotype in routine testing. RhD-positive (D+) RBC transfusion for patients with Asian-type DEL has been proposed but has not been generally adopted because of a lack of direct evidence regarding its safety and the underlying mechanism. We performed a single-arm multicenter clinical trial to document the outcome of D+ RBC transfusion in patients with Asian-type DEL; none of the recipients (0/42; 95% confidence interval, 0-8.40) developed alloanti-D after a median follow-up of 226 days. We conducted a large retrospective study to detect alloanti-D immunization in 4045 serologic D- pregnant women throughout China; alloanti-D was found only in individuals with true D- (2.63%, 79/3009), but not in those with Asian-type DEL (0/1032). We further retrospectively examined 127 serologic D- pregnant women who had developed alloanti-D and found none with Asian-type DEL (0/127). Finally, we analyzed RHD transcripts from Asian-type DEL erythroblasts and examined antigen epitopes expressed by various RHD transcripts in vitro, finding a low abundance of full-length RHD transcripts (0.18% of the total) expressing RhD antigens carrying the entire repertoire of epitopes, which could explain the immune tolerance against D+ RBCs. Our results provide multiple lines of evidence that individuals with Asian-type DEL cannot produce alloanti-D when exposed to D+ RBCs after transfusion or pregnancy. Therefore, we recommend considering D+ RBC transfusion and discontinuing anti-D prophylaxis in patients with Asian-type DEL, including pregnant women. This clinical trial is registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT03727230.
© 2023 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

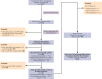
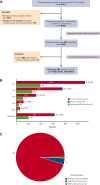
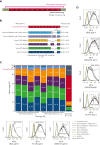
Comment in
-
Safe transfusion in Asian-type DEL.Blood. 2023 Apr 27;141(17):2044-2046. doi: 10.1182/blood.2023019646. Blood. 2023. PMID: 37103952 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kim JY, Kim SY, Kim CA, Yon GS, Park SS. Molecular characterization of D- Korean persons: development of a diagnostic strategy. Transfusion. 2005;45(3):345–352. - PubMed
-
- Luettringhaus TA, Cho D, Ryang DW, Flegel WA. An easy RHD genotyping strategy for D- East Asian persons applied to Korean blood donors. Transfusion. 2006;46(12):2128–2137. - PubMed
-
- Ogasawara K, Suzuki Y, Sasaki K, et al. Molecular basis for D- Japanese: identification of novel DEL and D- alleles. Vox Sang. 2015;109(4):359–365. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

