Multi-target activity of copper complexes: Antibacterial, DNA binding, and molecular docking with SARS-CoV-2 receptor
- PMID: 36639010
- PMCID: PMC9831667
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbi.2023.110349
Multi-target activity of copper complexes: Antibacterial, DNA binding, and molecular docking with SARS-CoV-2 receptor
Abstract
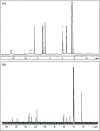
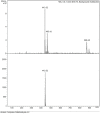
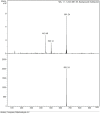
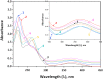
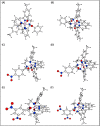
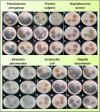
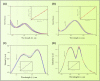
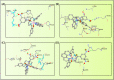
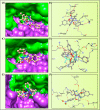
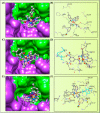
A series of pendant-armed mixed-ligand copper(II) complexes of the type [CuL1-3(diimine)] (1-6) have been synthesized by the reaction of pendant-armed ligands N,N-bis(2-(((E)-2-hydroxy-5-methylbenzylidene)amino)ethyl)benzamide (H2L1), N,N-bis(2-(((E)-2-hydroxy-5-methylbenzylidene)amino)ethyl)-4-nitrobenzamide (H2L2) and N,N-bis(2-(((E)-2-hydroxy-5-methylbenzylidene)amino)ethyl)-3,5-dinitrobenzamide (H2L3) with diimine = 2,2'-bipyridyl (bpy) or 1,10-phenanthroline (phen) in the presence of copper(II) chloride and analyzed using various spectroscopic methods. All the spectroscopic results support that the complexes adopt a pentagonal-bipyramidal shape around the copper ion. Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria were used to test all the complexes for antibacterial activity and all the complexes had greater potency against gram-negative pathogens. DNA-binding experiments of complexes with calf thymus DNA revealed a major-groove binding pattern, further supported by molecular docking studies. Complexes have significantly interacted with SARS-CoV-2 receptor via π-π, π-σ, π-alkyl, π-anion, π-cation, alkyl, hydrogen bond, van der Waals, and electrostatic interactions. The estimated binding energy and inhibition constant of these complexes are higher than standard drugs, chloroquine, and molnupiravir.
Keywords: Antibacterial; DNA interactions; Mixed-ligand complexes; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Abdelhamid H.N., Wu H.-F. A method to detect metal–drug complexes and their interactions with pathogenic bacteria via graphene nanosheet assist laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry and biosensors. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2012;751:94–104. - PubMed
-
- Cao Q., Li Y., Freisinger E., Qin P.Z., Sigel R.K.O., Mao Z.W. G-quadruplex DNA targeted metal complexes acting as potential anticancer drugs. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2017;4(1):10–32.
-
- Trudu F., Amato F., Vaňhara P., Pivetta T., Peña-Méndez E., Havel J. Coordination compounds in cancer: past, present and perspectives. J. Appl. Biomed. 2015;13(2):79–103.
-
- Mahendiran D., Gurumoorthy P., Gunasekaran K., Kumar R.S., Rahiman A.K. Structural modeling, in vitro antiproliferative activity, and the effect of substituents on the DNA fastening and scission actions of heteroleptic copper (II) complexes with terpyridines and naproxen. New J. Chem. 2015;39(10):7895–7911.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

