Efficacy of luteolin on the human gastric cancer cell line MKN45 and underlying mechanism
- PMID: 36639993
- PMCID: PMC9924784
- DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2023.01.005
Efficacy of luteolin on the human gastric cancer cell line MKN45 and underlying mechanism
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the antitumour efficacy of luteolin on gastric cancer (GC) and study the mechanism underpinning the action.
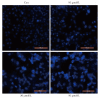
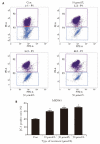
Methods: Effects of luteolin on cell growth inhibition, apoptosis, and cell cycle arrest in MKN45 cells were investigated using the cell counting kit-8 assay. Changes in the mitochondrial membrane potential after luteolin treatment were assessed using 5,5',6,6'-tetra-chloro-1,1',3,3'-tetraethylbenzimidazolcarbocyanineiodi-de (JC-1) staining. To investigate whether apoptotic effect by luteolin is related to the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene (PI3K/Akt) pathway, cells were additionally treated with LY294002, a PI3K/Akt pathway inhibitor. Moreover, the expressions of apoptosis-related proteins, namely B-cell lymphoma 2(Bcl-2), Bcl-2 associated X protein (Bax), Akt, p-Akt, caspase-3, and cytochrome C, were detected after luteolin treatment.
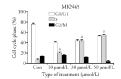
Results: The study revealed that in MKN45 cells, luteolin could inhibit the cell proliferation in a time- and dose-dependent manner; block the cell cycle in the S-phase; induce apoptosis; reduce the mitochondrial membrane potential; increase the expression of Bax, caspase-3, and cytochrome C; and decrease the expression of Bcl-2 and p-Akt. Luteolin might be involved in the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway, indicating that this pathway could be a therapeutic target for GC treatment.
Conclusion: Luteolin could inhibit the proliferation of GC cells and block the cell cycle in the S-phase. The mechanism of inducing apoptosis in these cells was related to the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway.
Keywords: Akt; apoptosis; luteolin; phosphoinositide 3-kinase; signal transduction; stomach neoplasms.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Piperine Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis of Human Gastric Cancer Cells by Downregulating Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase (PI3K)/Akt Pathway.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Dec 31;26:e928403. doi: 10.12659/MSM.928403. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 33382670 Free PMC article.
-
Alisol B acetate induces apoptosis of SGC7901 cells via mitochondrial and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases/Akt signaling pathways.World J Gastroenterol. 2009 Jun 21;15(23):2870-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.2870. World J Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 19533808 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the PI3K/Akt pathway increases the chemosensitivity of gastric cancer to vincristine.Oncol Rep. 2013 Aug;30(2):773-82. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2520. Epub 2013 Jun 5. Oncol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23743572
-
Effects and Mechanisms of Luteolin, a Plant-Based Flavonoid, in the Prevention of Cancers via Modulation of Inflammation and Cell Signaling Molecules.Molecules. 2024 Feb 29;29(5):1093. doi: 10.3390/molecules29051093. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38474604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural products targeting signaling pathways associated with regulated cell death in gastric cancer: Recent advances and perspectives.Phytother Res. 2023 Jun;37(6):2661-2692. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7866. Epub 2023 May 8. Phytother Res. 2023. PMID: 37157181 Review.
Cited by
-
Flavonoids and Gastric Cancer Therapy: From Signaling Pathway to Therapeutic Significance.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Jul 25;18:3233-3253. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S466470. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39081701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent insights into luteolin and its biological and pharmacological activities.EXCLI J. 2024 May 16;23:787-794. doi: 10.17179/excli2024-7168. eCollection 2024. EXCLI J. 2024. PMID: 39165588 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Efficacy and safety of Piwei Peiyuan Prescription in the treatment of chronic atrophic gastritis: A multicenter, double-blind, double-simulated, randomized, controlled clinical trial.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 May 10;103(19):e37981. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037981. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38728508 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Microplastics as Emerging Contaminants and Human Health: Exploring Functional Nutrition in Gastric-Colon-Brain Axis Cancer.Toxics. 2025 May 26;13(6):438. doi: 10.3390/toxics13060438. Toxics. 2025. PMID: 40559911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Metastasis by Luteolin in Human Bladder Cancer EJ138 Cells: An Experimental Study.Iran J Pharm Res. 2024 Nov 16;23(1):e153408. doi: 10.5812/ijpr-153408. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Iran J Pharm Res. 2024. PMID: 40066127 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin 2019; 69: 7-34. - PubMed
-
- Dai ZJ, Gao J, . Ji ZZ, et al. Matrine induces apoptosis in gastric carcinoma cells via alteration of Fas/FasL and activation of caspase-3. J Ethnopharmacol 2009; 123: 91-6. - PubMed
-
- Davern M, Lysaght J. Cooperation between chemotherapy and immunotherapy in gastroesophageal cancers-ScienceDirect. Cancer Lett 2020; 495: 89-99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
