Single-cell RNA sequencing identifies a population of human liver-type ILC1s
- PMID: 36640314
- PMCID: PMC9950534
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111937
Single-cell RNA sequencing identifies a population of human liver-type ILC1s
Abstract
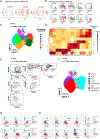
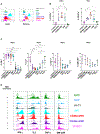
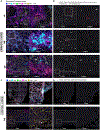
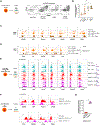
Group 1 innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) comprise a heterogeneous family of cytotoxic natural killer (NK) cells and ILC1s. We identify a population of "liver-type" ILC1s with transcriptional, phenotypic, and functional features distinct from those of conventional and liver-resident NK cells as well as from other previously described human ILC1 subsets. LT-ILC1s are CD49a+CD94+CD200R1+, express the transcription factor T-BET, and do not express the activating receptor NKp80 or the transcription factor EOMES. Similar to NK cells, liver-type ILC1s produce IFN-γ, TNF-α, and GM-CSF; however, liver-type ILC1s also produce IL-2 and lack perforin and granzyme-B. Liver-type ILC1s are expanded in cirrhotic liver tissues, and they can be produced from blood-derived ILC precursors in vitro in the presence of TGF-β1 and liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. Cells with similar signature and function can also be found in tonsil and intestinal tissues. Collectively, our study identifies and classifies a population of human cross-tissue ILC1s.
Keywords: CP: Immunology; ILC1; TGF-β; cirrhotic liver; cross-tissue ILC1; human group 1 ILC; innate lymphoid cell; liver ILC1; liver environment; natural killer cell.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

