The Impact of Lymphedema on Patient-Reported Outcomes After Breast Reconstruction: A Preliminary Propensity Score-Matched Analysis
- PMID: 36641512
- PMCID: PMC11071662
- DOI: 10.1245/s10434-022-12994-z
The Impact of Lymphedema on Patient-Reported Outcomes After Breast Reconstruction: A Preliminary Propensity Score-Matched Analysis
Abstract
Background: Studies on the impact of secondary lymphedema on patient-reported satisfaction and quality of life following postmastectomy breast reconstruction are limited by their heterogeneity. We aimed to reduce heterogeneity in study sample populations and compare BREAST-Q Reconstruction Module scores of patients with lymphedema matched to patients without lymphedema.
Methods: We identified patients who underwent postmastectomy breast reconstruction from 2009 to 2017 and performed a propensity score-matched analysis to compare patient-reported outcomes of patients who developed lymphedema with those who did not. Matched covariates included age, body mass index, race/ethnicity, smoking history, radiation or chemotherapy exposure, postoperative infection, and reconstruction modality and laterality. Outcomes of interest were pre- and postoperative BREAST-Q scores for Satisfaction with Breasts, Physical Well-being of the Chest, Sexual Well-Being, and Psychosocial Well-Being; the minimal clinically important difference (MCID) was four points.
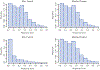
Results: Matched cohorts included 322 patients per group. Preoperative BREAST-Q scores did not differ between lymphedema and non-lymphedema matched cohorts. Postoperative BREAST-Q scores were significantly lower in lymphedema patients: Physical Well-Being of the Chest (all time points), Satisfaction with Breast (at 1 and 2 years), Sexual Well-Being (at 2 years), and Psychosocial Well-Being (at 2 and 3 years). All significant differences in average scores were greater than the MCID.
Conclusions: Patients with breast cancer-related lymphedema reported significantly lower Physical Well-Being of the Chest, Satisfaction with Breasts, Sexual Well-Being, and Psychosocial Well-Being at various time points. Our findings may prove useful for patient counseling and justify the need for further research on the prevention and treatment of this devastating disease.
© 2023. Society of Surgical Oncology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quality of Life in Breast Reconstruction Patients after Irradiation to Tissue Expander: A Propensity-Matched Preliminary Analysis.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2023 Aug 1;152(2):259-269. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000010249. Epub 2023 Feb 1. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2023. PMID: 36724013 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term Patient-Reported Outcomes in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction.JAMA Surg. 2018 Oct 1;153(10):891-899. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2018.1677. JAMA Surg. 2018. PMID: 29926096 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Evolution of Breast Satisfaction and Well-Being after Breast Cancer: A Propensity-Matched Comparison to the Norm.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020 Mar;145(3):595-604. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000006535. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020. PMID: 32097289 Free PMC article.
-
Outcome of Quality of Life for Women Undergoing Autologous versus Alloplastic Breast Reconstruction following Mastectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020 May;145(5):1109-1123. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000006720. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020. PMID: 32332522
-
A Systematic Review of the Impact of Patient Factors on BREAST-Q Outcomes After Reduction Mammoplasty.Ann Plast Surg. 2023 Jun 1;90(6S Suppl 5):S667-S673. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000003471. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Ann Plast Surg. 2023. PMID: 37399487
Cited by
-
Association Between Symptom Burden and Early Lymphatic Abnormalities After Regional Nodal Irradiation for Breast Cancer.Pract Radiat Oncol. 2024 May-Jun;14(3):e180-e189. doi: 10.1016/j.prro.2023.10.008. Epub 2023 Oct 31. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2024. PMID: 37914083 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced risk of lymphedema after immediate breast reconstruction in breast cancer: a retrospective nationwide study.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 5;15(1):28584. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-10430-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40764520 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of Life and Minimal Clinically Important Difference in Colorectal Cancer Patients Undergoing Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy: A Large Prospective Cohort Study.Ann Surg Oncol. 2025 Aug 28. doi: 10.1245/s10434-025-18147-2. Online ahead of print. Ann Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40877723
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical