HPC+ in the medical field: Overview and current examples
- PMID: 36641699
- PMCID: PMC10357138
- DOI: 10.3233/THC-229015
HPC+ in the medical field: Overview and current examples
Abstract
Background: To say data is revolutionising the medical sector would be a vast understatement. The amount of medical data available today is unprecedented and has the potential to enable to date unseen forms of healthcare. To process this huge amount of data, an equally huge amount of computing power is required, which cannot be provided by regular desktop computers. These areas can be (and already are) supported by High-Performance-Computing (HPC), High-Performance Data Analytics (HPDA), and AI (together "HPC+").
Objective: This overview article aims to show state-of-the-art examples of studies supported by the National Competence Centres (NCCs) in HPC+ within the EuroCC project, employing HPC, HPDA and AI for medical applications.
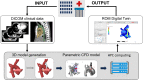
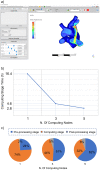
Method: The included studies on different applications of HPC in the medical sector were sourced from the National Competence Centres in HPC and compiled into an overview article. Methods include the application of HPC+ for medical image processing, high-performance medical and pharmaceutical data analytics, an application for pediatric dosimetry, and a cloud-based HPC platform to support systemic pulmonary shunting procedures.
Results: This article showcases state-of-the-art applications and large-scale data analytics in the medical sector employing HPC+ within surgery, medical image processing in diagnostics, nutritional support of patients in hospitals, treating congenital heart diseases in children, and within basic research.
Conclusion: HPC+ support scientific fields from research to industrial applications in the medical area, enabling researchers to run faster and more complex calculations, simulations and data analyses for the direct benefit of patients, doctors, clinicians and as an accelerator for medical research.
Keywords: AI (artificial intelligence); Computer simulation; computational modeling; data analysis; diagnosis; medicine; therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
None to report.
Figures



References
-
- NVIDIA Clara Imaging. https://developer.nvidia.com/clara-medical-imaging (2020).
-
- NIfTI: Neuroimaging Informatics Technology Initiative. https://nifti.nimh.nih.gov/ (2021).
-
- VIPUN Medical, 2022, accessed 20/10/2022, https://www.vipunmedical.com/#about.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

