The Tick-Borne Pathogens: An Overview of China's Situation
- PMID: 36642777
- PMCID: PMC9841149
- DOI: 10.1007/s11686-023-00658-1
The Tick-Borne Pathogens: An Overview of China's Situation
Abstract
Background: Ticks are important medical arthropods that can transmit hundreds of pathogens, such as parasites, bacteria, and viruses, leading to serious public health burdens worldwide. Unexplained fever is the most common clinical manifestation of tick-borne diseases. Since the emergence of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the surge of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) cases led to the hospital overload and fewer laboratory tests for tick-borne diseases. Therefore, it is essential to review the tick-borne pathogens and further understand tick-borne diseases.
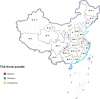
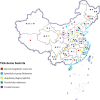
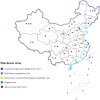
Purpose: The geographic distribution and population of ticks in the Northern hemisphere have expanded while emerging tick-borne pathogens have been introduced to China continuously. This paper focused on the tick-borne pathogens that are threatening public health in the world. Their medical significant tick vectors, as well as the epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and control measures, are emphasized in this document.
Methods: In this study, all required data were collected from articles indexed in English databases, including Scopus, PubMed, Web of Science, Science Direct, and Google Scholar.
Results: Ticks presented a great threat to the economy and public health. Although both infections by tick-borne pathogens and SARS-CoV-2 have fever symptoms, the history of tick bite and its associated symptoms such as encephalitis or eschar could be helpful for the differential diagnosis. Additionally, as a carrier of vector ticks, migratory birds may play a potential role in the geographical expansion of ticks and tick-borne pathogens during seasonal migration.
Conclusion: China should assess the risk score of vector ticks and clarify the potential role of migratory birds in transmitting ticks. Additionally, the individual and collective protection, vector control, comprehensive surveillance, accurate diagnosis, and symptomatic treatment should be carried out, to meet the challenge.
Keywords: Bacteria; Parasite; Pathogen; Tick; Tick-borne pathogens; Virus.
© 2023. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to Witold Stefański Institute of Parasitology, Polish Academy of Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Screening for multiple tick-borne pathogens in Ixodes ricinus ticks from birds in Denmark during spring and autumn migration seasons.Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2019 Apr;10(3):546-552. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2019.01.007. Epub 2019 Jan 24. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2019. PMID: 30709658
-
Transport of ixodid ticks and tick-borne pathogens by migratory birds.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2013 Sep 10;3:48. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2013.00048. eCollection 2013. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24058903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tick-borne pathogens in ticks collected from birds in Taiwan.Parasit Vectors. 2017 Nov 25;10(1):587. doi: 10.1186/s13071-017-2535-4. Parasit Vectors. 2017. PMID: 29178908 Free PMC article.
-
[Epidemiology of pathogenic tick-borne viruses in China: a review].Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2023 Oct 11;35(4):325-330. doi: 10.16250/j.32.1374.2023128. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37926466 Review. Chinese.
-
Emerging Tick-Borne Diseases.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2020 Jan 2;33(2):e00083-18. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00083-18. Print 2020 Mar 18. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2020. PMID: 31896541 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Detection of Tick-Borne Pathogens in Kumasi: With a First Report of Zoonotic Pathogens in Abattoir Workers.Biomed Res Int. 2024 Jul 14;2024:4848451. doi: 10.1155/2024/4848451. eCollection 2024. Biomed Res Int. 2024. PMID: 39035771 Free PMC article.
-
Tick Control Strategies: Critical Insights into Chemical, Biological, Physical, and Integrated Approaches for Effective Hard Tick Management.Vet Sci. 2025 Feb 2;12(2):114. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12020114. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40005873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering the microbial communities in ticks of Inner Mongolia: ecological determinants and pathogen profiles.Parasit Vectors. 2024 Nov 4;17(1):448. doi: 10.1186/s13071-024-06512-1. Parasit Vectors. 2024. PMID: 39497080 Free PMC article.
-
HL-IR mediates cinnamaldehyde repellency behavior in parthenogenetic Haemaphysalis longicornis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2025 Mar 17;19(3):e0012877. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012877. eCollection 2025 Mar. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2025. PMID: 40096053 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial diversity of ticks and a novel typhus group Rickettsia species (Rickettsiales bacterium Ac37b) in Inner Mongolia, China.Parasite. 2023;30:58. doi: 10.1051/parasite/2023057. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Parasite. 2023. PMID: 38084939 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2020NY-017/Key Research and Development Projects of Shaanxi Province
- XN14/the Animal Husbandry Special fund of Department of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of Shaanxi Province
- SKLVEB2019KFKT007/the State Key Laboratory of Veterinary Etiological Biology, Lanzhou Veterinary Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous