CEO's Childhood Experience of Natural Disaster and CSR Activities
- PMID: 36643014
- PMCID: PMC9821374
- DOI: 10.1007/s10551-022-05319-3
CEO's Childhood Experience of Natural Disaster and CSR Activities
Abstract
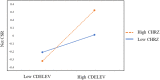
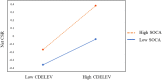
Interest in the drivers of firms' corporate social responsibility (CSR) is growing. However, little is known about the influence of a CEO's childhood experience of natural disasters on CSR. Using archival data, we explore this relationship by offering three mechanisms that may account for how the CEO's childhood experience of natural disaster is related to their CSR. More specifically, while prior research has established a positive relationship based on the post-traumatic growth theory, we show that the dual mechanisms of prosocial values and a CEO's risk aversion explain the positive relationship. We further find that the positive relationship is stronger (1) when CEOs have longer career horizons and (2) when community social capital is high. This study contributes to both research and managerial implications on the topics of CEO's childhood experience and CSR. In particular, this study advances the upper echelon theory by revealing that a CEO's childhood experience of natural disaster is a useful yet relatively underexplored variable that can help explain the substantial variations in firms' CSR. Moreover, we emphasize that a CEO's career horizons and level of community social capital are important variables that further amplify the effect of a CEO's childhood experience of natural disaster on the firm's CSR commitment.
Keywords: CEO; CEO career horizon; CSR; Childhood experience; Natural disaster; Social capital.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature B.V. 2023, Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Adhikari BK. Causal effect of analyst following on corporate social responsibility. Journal of Corporate Finance. 2016;41:201–216. doi: 10.1016/j.jcorpfin.2016.08.010. - DOI
-
- Adhikari BK. Female executives and corporate cash holdings. Applied Economics Letters. 2018;25(13):958–963. doi: 10.1080/13504851.2017.1388904. - DOI
-
- Al-Shammari M, Rasheed A, Al-Shammari HA. CEO narcissism and corporate social responsibility: Does CEO narcissism affect CSR focus? Journal of Business Research. 2019;104:106–117. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.07.005. - DOI
-
- Anderson JD, Core JE. Managerial incentives to increase risk provided by debt, stock, and options. Management Science. 2018;64(9):4408–4432. doi: 10.1287/mnsc.2017.2811. - DOI
-
- Antia M, Pantzalis C, Park JC. CEO decision horizon and firm performance: An empirical investigation. Journal of Corporate Finance. 2010;16(3):288–301. doi: 10.1016/j.jcorpfin.2010.01.005. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources