Augmented Intelligence to Identify Patients With Advanced Heart Failure in an Integrated Health System
- PMID: 36643021
- PMCID: PMC9838119
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacadv.2022.100123
Augmented Intelligence to Identify Patients With Advanced Heart Failure in an Integrated Health System
Abstract
Background: Timely referral for specialist evaluation in patients with advanced heart failure (HF) is a Class 1 recommendation. However, the transition from stage C HF to advanced or stage D HF often goes undetected in routine care, resulting in delayed referral and higher mortality rates.
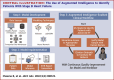
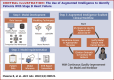
Objectives: The authors sought to develop an augmented intelligence-enabled workflow using machine learning to identify patients with stage D HF and streamline referral.
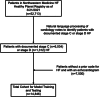
Methods: We extracted data on HF patients with encounters from January 1, 2007, to November 30, 2020, from a HF registry within a regional, integrated health system. We created an ensemble machine learning model to predict stage C or stage D HF and integrated the results within the electronic health record.
Results: In a retrospective data set of 14,846 patients, the model had a good positive predictive value (60%) and low sensitivity (25%) for identifying stage D HF in a 100-person, physician-reviewed, holdout test set. During prospective implementation of the workflow from April 1, 2021, to February 15, 2022, 416 patients were reviewed by a clinical coordinator, with agreement between the model and the coordinator in 50.3% of stage D predictions. Twenty-four patients have been scheduled for evaluation in a HF clinic, 4 patients started an evaluation for advanced therapies, and 1 patient received a left ventricular assist device.
Conclusions: An augmented intelligence-enabled workflow was integrated into clinical operations to identify patients with advanced HF. Endeavors such as this require a multidisciplinary team with experience in design thinking, informatics, quality improvement, operations, and health information technology, as well as dedicated resources to monitor and improve performance over time.
Keywords: advanced heart failure; artificial intelligence; augmented intelligence; electronic health record; integrated healthcare system; machine learning.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Ahmad was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (K23HL155970) and the American Heart Association (AHA number 856917); and has received consulting fees from Teladoc Livongo and Pfizer unrelated to this manuscript. All other authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures


Comment in
-
Can Machines Find the Sweet Spot in End-Stage Heart Failure?JACC Adv. 2022 Oct 28;1(4):100122. doi: 10.1016/j.jacadv.2022.100122. eCollection 2022 Oct. JACC Adv. 2022. PMID: 38939701 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tsao C.W., Aday A.W., Almarzooq Z.I., et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2022 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2022;145:e153–e639. - PubMed
-
- Morris A.A., Khazanie P., Drazner M.H., et al. Guidance for timely and appropriate referral of patients with advanced heart failure: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021;144(15):e238–e250. - PubMed
-
- Kalogeropoulos A.P., Samman-Tahhan A., Hedley J.S., et al. Progression to stage D heart failure among outpatients with stage C heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. J Am Coll Cardiol HF. 2017;5:528–537. - PubMed
-
- Heidenreich P.A., Bozkurt B., Aguilar D., et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA guideline for the management of heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022;79(17):e263–e421. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

