New Staging Model for Radiation-based Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment: A National Multicenter Study
- PMID: 36643048
- PMCID: PMC9817045
- DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2022.00002
New Staging Model for Radiation-based Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment: A National Multicenter Study
Abstract
Background and aims: The study aimed to create a new staging model for radiotherapy-based treatment for prognostic hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) classification.
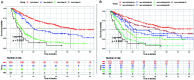
Methods: The training cohort comprised 658 patients receiving stereotactic body radiotherapy and external validation cohort comprised 533 patients receiving three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy and intensity-modulated radiotherapy. We established a modified staging system as follows: stage I, solitary nodule without macrovascular invasion, or 2-3 nodules no more than 3.0 cm apart, and performance status (PS) 0-2 (Ia: ALBI-1 grade; Ib: ALBI-2 or 3 grade); stage II: 2-3 nodules with any one nodule more than 3.0-cm apart, or ≥4 nodules, and performance status 0-2 (IIa: ALBI-1 grade; IIb: ALBI-2 grade); stage III: macrovascular invasion, regional lymph node metastasis or distant metastasis, and performance status 0-2 (IIIa: ALBI-1 grade; IIIb: ALBI-2 grade); stage IV: performance status 3-4, or performance status 0-2 with ALBI-3 grade. We analyzed long-term overall survival based on different stages.
Results: The staging model showed an excellent ability to discriminate patients according to four stages and seven substages with notably different curves in the training and validation cohort. The median survival decreased from stages I to IV with 63.0 months in stage I (not reached in Ia, and 53.0 months in Ib), 24.0 months in stage II (28.0 months in IIa, and 22.0 months in IIb), 11.0 months in stage III (18.0 months in IIIa, and 9.0 months in IIIb), and less than 9.0 months in stage IV in the training cohort.
Conclusions: The modified staging model may provide an alternative for clinical radiation oncologists.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Overall survival; Radiotherapy; Staging system; Stereotactic body radiotherapy.
© 2023 Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest related to this publication.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prognosis and survival after resection for bronchogenic carcinoma based on the 1997 TNM-staging classification: the Japanese experience.Ann Thorac Surg. 2001 Jun;71(6):1759-64. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(00)02609-6. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001. PMID: 11426744
-
Modified staging system for extremity soft tissue sarcomas.Ann Surg Oncol. 1999 Jan-Feb;6(1):57-69. doi: 10.1007/s10434-999-0057-9. Ann Surg Oncol. 1999. PMID: 10030416
-
Validation and prognostic value of EZ-ALBI score in patients with intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma treated with trans-arterial chemoembolization.BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 Jun 14;22(1):295. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02366-y. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35701739 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and albumin bilirubin grade in hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Sep 7;26(33):5022-5049. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i33.5022. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32952347 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of the albumin-bilirubin grade in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and other liver diseases.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Apr;8(8):553. doi: 10.21037/atm.2020.02.116. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32411776 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Black Phosphorus Nanosheets-Loaded Single-Atom Gold Nanoenzymes for Enhanced Photodynamic Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Nov 26;19:12583-12592. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S414938. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39624119 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive Factors and Nomogram (MAP-BNP) for Post Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy Survival in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2025 Sep-Oct;15(5):102555. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2025.102555. Epub 2025 Mar 28. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 40292336
-
Radiomics of Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI for Predicting Radiation-Induced Hepatic Toxicity After Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Machine Learning Predictive Model Based on the SHAP Methodology.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2025 May 17;12:999-1015. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S523448. eCollection 2025. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2025. PMID: 40406666 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a nomogram for radiation-induced hepatic toxicity after intensity modulated radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2024 Jun 1;54(6):699-707. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyae024. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38376811 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Korean Liver Cancer Association (KLCA) and National Cancer Center (NCC), Goyang, Korea 2018 Korean Liver Cancer Association-National Cancer Center Korea Practice Guidelines for the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Korean J Radiol. 2019;20(7):1042–1113. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2019.0140. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Takeda A, Sanuki N, Tsurugai Y, Iwabuchi S, Matsunaga K, Ebinuma H, et al. Phase 2 study of stereotactic body radiotherapy and optional transarterial chemoembolization for solitary hepatocellular carcinoma not amenable to resection and radiofrequency ablation. Cancer. 2016;122(13):2041–2049. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30008. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
