Capparis zeylanica L. root extract promotes apoptosis and cell cycle arrest, inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and triggers E-cadherin expression in breast cancer cell lines
- PMID: 36643403
- PMCID: PMC9832210
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-023-03461-x
Capparis zeylanica L. root extract promotes apoptosis and cell cycle arrest, inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and triggers E-cadherin expression in breast cancer cell lines
Abstract
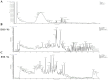
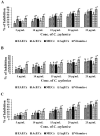
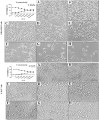
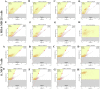
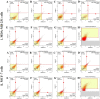
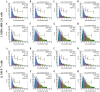
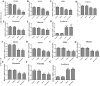
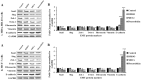
Capparis zeylanica L. is a climbing shrub distributed in Indian subcontinent and Mediterranean region. Almost all parts of the plant are used in folk medicine and traditional practices to treat several human ailments. The present study was aimed to investigate the role of C. zeylanica L. root extract in preventing cancerous cells growth and proliferation, as well as promoting apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Methanolic extract of C. zeylanica L. (MECz) was prepared and characterized by LC-ESI-MS/MS analysis. In vitro cytotoxicity and anti-proliferative activity of MECz was evaluated by MTT assay, while cell viability, apoptosis and cell cycle progression by Muse Cell analyzer. Furthermore, the mRNA and protein expressions of EMT markers were assessed using qRT-PCR and western blotting techniques, respectively. The MECz was found to be rich in phenolic compounds including chlorogenic acid, 6-gingerol, and certain triterpenes like ursolic acid etc. The apparent anti-metastasis activity of MECz was evident from IC50 value of 19.12 and 24.22 μg/mL, respectively, on MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells in MTT assay. An absolute decrease in cell viability (78.1-53.4% and 89.9-49.0%), augmented apoptosis (90.98-48.25% and 88.25-47.70%) and S phase, G2/M phase cell cycle arrest was found by MECz treatment on MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells. The gene expression studies revealed that MECz could significantly (p < 0.001) regulate the expression of EMT markers such as snail, slug, zeb-1, twist-1, fibronectin, vimentin and E-cadherin at molecular level. These findings demonstrate that C. zeylanica L. root extract inhibits breast cancer cells growth and proliferation through regulating the expression of key EMT marker genes and proteins. Thus, MECz may be suggested as a potential anti-metastasis agent in the treatment of breast cancer.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Breast cancer; Capparis zeylanica; Cell cycle; Cytotoxicity; EMT markers.
© King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology 2023, Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ursolic acid regulates key EMT transcription factors, induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 breast cancer cells, an in-vitro and in silico studies.J Cell Biochem. 2023 Dec;124(12):1900-1918. doi: 10.1002/jcb.30496. Epub 2023 Nov 22. J Cell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 37992132
-
New halogenated constituents from Mangifera zeylanica Hook.f. and their potential anti-cancer effects in breast and ovarian cancer cells.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Aug 2;189:165-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.05.047. Epub 2016 May 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27224244
-
Hypericum roeperianum bark extract suppresses breast cancer proliferation via induction of apoptosis, downregulation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling cascade and reversal of EMT.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jan 30;319(Pt 1):117093. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117093. Epub 2023 Aug 25. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37634746
-
A study of the potential anticancer activity of Mangifera zeylanica bark: Evaluation of cytotoxic and apoptotic effects of the hexane extract and bioassay-guided fractionation to identify phytochemical constituents.Oncol Lett. 2016 Feb;11(2):1335-1344. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4087. Epub 2016 Jan 8. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 26893740 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacology, phytochemistry and toxicity of Helminthostachys zeylanica: a review.Nat Prod Res. 2024 Dec 3:1-12. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2024.2429521. Online ahead of print. Nat Prod Res. 2024. PMID: 39628108 Review.
Cited by
-
Uvaol attenuates TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human alveolar epithelial cells by modulating expression and membrane localization of β-catenin.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 7;15:1504556. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1504556. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39840107 Free PMC article.
-
Novel sulfamethoxazole and 1-(2-fluorophenyl) piperazine derivatives as potential apoptotic and antiproliferative agents by inhibition of BCL2; design, synthesis, biological evaluation, and docking studies.3 Biotech. 2024 Nov;14(11):269. doi: 10.1007/s13205-024-04111-6. Epub 2024 Oct 15. 3 Biotech. 2024. PMID: 39421851
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

