A new order, Entrophosporales, and three new Entrophospora species in Glomeromycota
- PMID: 36643412
- PMCID: PMC9835108
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.962856
A new order, Entrophosporales, and three new Entrophospora species in Glomeromycota
Abstract
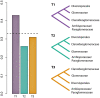
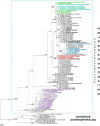
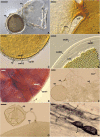
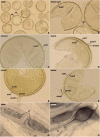
As a result of phylogenomic, phylogenetic, and morphological analyses of members of the genus Claroideoglomus, four potential new glomoid spore-producing species and Entrophospora infrequens, a new order, Entrophosporales, with one family, Entrophosporaceae (=Claroideoglomeraceae), was erected in the phylum Glomeromycota. The phylogenomic analyses recovered the Entrophosporales as sister to a clade formed by Diversisporales and Glomeraceae. The strongly conserved entrophosporoid morph of E. infrequens, provided with a newly designated epitype, was shown to represent a group of cryptic species with the potential to produce different glomoid morphs. Of the four potential new species, three enriched the Entrophosporales as new Entrophospora species, E. argentinensis, E. glacialis, and E. furrazolae, which originated from Argentina, Sweden, Oman, and Poland. The fourth fungus appeared to be a glomoid morph of the E. infrequens epitype. The physical association of the E. infrequens entrophosporoid and glomoid morphs was reported and illustrated here for the first time. The phylogenetic analyses, using nuc rDNA and rpb1 concatenated sequences, confirmed the previous conclusion that the genus Albahypha in the family Entrophosporaceae sensu Oehl et al. is an unsupported taxon. Finally, the descriptions of the Glomerales, Entrophosporaceae, and Entrophospora were emended and new nomenclatural combinations were introduced.
Keywords: Claroideoglomus; arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi; four new taxa; morphology; new combinations; nuc rDNA; phylogenomic and phylogenetic taxonomy; rpb1.
Copyright © 2022 Błaszkowski, Sánchez-García, Niezgoda, Zubek, Fernández, Vila, Al-Yahya’ei, Symanczik, Milczarski, Malinowski, Cabello, Goto, Casieri, Malicka, Bierza and Magurno.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors FF and AV were employed by R&D Department, Symborg SL. Author LC was employed by Mycorrhizal Applications LLC at Bio-Research and Development Growth Park. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Revision of Entrophosporales, with Three Genera and an Identification Key for All Species Currently Attributed to This Order.J Fungi (Basel). 2025 Jan 26;11(2):97. doi: 10.3390/jof11020097. J Fungi (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39997391 Free PMC article.
-
New Glomeromycotan Taxa, Dominikia glomerocarpica sp. nov. and Epigeocarpum crypticum gen. nov. et sp. nov. From Brazil, and Silvaspora gen. nov. From New Caledonia.Front Microbiol. 2021 Apr 23;12:655910. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.655910. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33967994 Free PMC article.
-
Three new species of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (Glomeromycota) and Acaulospora gedanensis revised.Front Microbiol. 2024 Feb 12;15:1320014. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1320014. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38410392 Free PMC article.
-
A history of the taxonomy and systematics of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi belonging to the phylum Glomeromycota.Mycorrhiza. 2012 May;22(4):247-58. doi: 10.1007/s00572-012-0432-4. Epub 2012 Mar 6. Mycorrhiza. 2012. PMID: 22391803 Review.
-
A Systematic Review of the Effects of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi on Root-Lesion Nematodes, Pratylenchus spp.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Jul 14;11:923. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00923. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32765542 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Phylogenetic classification of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: new species and higher-ranking taxa in Glomeromycota and Mucoromycota (class Endogonomycetes).MycoKeys. 2024 Aug 9;107:273-325. doi: 10.3897/mycokeys.107.125549. eCollection 2024. MycoKeys. 2024. PMID: 39169987 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of plant species, mycorrhizal inoculant, and soil phosphorus level on arbuscular mycorrhizal communities in onion and carrot roots.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Jan 15;14:1324626. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1324626. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38288412 Free PMC article.
-
Drastic mycorrhizal community shifts in Sceptridium ferns during the generation transition from fully mycoheterotrophic gametophytes to photosynthetic sporophytes.New Phytol. 2025 Feb;245(4):1705-1717. doi: 10.1111/nph.20330. Epub 2024 Dec 7. New Phytol. 2025. PMID: 39645585 Free PMC article.
-
Functional traits of Asteraceae species vary with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal identity and phylogeny.Mycorrhiza. 2025 Jun 5;35(3):40. doi: 10.1007/s00572-025-01214-7. Mycorrhiza. 2025. PMID: 40471452
-
Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi as Biostimulant and Biocontrol Agents: A Review.Microorganisms. 2024 Jun 24;12(7):1281. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12071281. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39065050 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ames R. N., Schneider R. W. (1979). Entrophospora, a new genus in the Endogonaceae. Mycotaxon 8 347–352.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

