Integrative Proteomic and Phosphoproteomic Analyses Revealed the Regulatory Mechanism of the Response to Ultraviolet B Stress in Clematis terniflora DC
- PMID: 36643485
- PMCID: PMC9835548
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.2c07258
Integrative Proteomic and Phosphoproteomic Analyses Revealed the Regulatory Mechanism of the Response to Ultraviolet B Stress in Clematis terniflora DC
Abstract
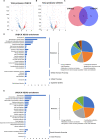
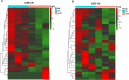
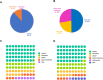
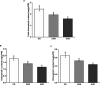
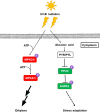
Clematis terniflora DC. (C. terniflora) has been used as an ancient Chinese traditional herbal medicine. The active substances in C. terniflora have been confirmed to be effective in treating diseases such as prostatitis. UV light radiation is a common environmental factor that damages plants and influences primary and secondary metabolism. Previous studies showed that ultraviolet B (UV-B) radiation followed by dark stress resulted in the accumulation of secondary metabolites in C. terniflora leaves. An in-depth understanding of how C. terniflora leaves respond to UV-B stress is crucial for improving C. terniflora value. Here, we conducted label-free proteomic and phosphoproteomic analyses to explore the protein changes under UV-B and UV-B combined with dark treatment. A total of 2839 proteins and 1638 phosphorylated proteins were identified. Integrative omics revealed that the photosynthetic system and carbohydrate balance were modulated under both stresses. The phosphoproteomic data indicated that the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway was triggered, while the abundance of phosphorylated proteins related to osmotic stress was increased under UV-B stress. Differentially abundant phosphoproteins from UV-B followed by dark treatment were mainly enriched in response to stimulus including calcium-mediated proteins. This study provides new insight into the impact of UV-B stress on C. terniflora and plant molecular resistance mechanisms through proteomic and phosphoproteomic analyses.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial proteomic analysis reveals the regulation of energy metabolism and reactive oxygen species production in Clematis terniflora DC. leaves under high-level UV-B radiation followed by dark treatment.J Proteomics. 2022 Mar 15;254:104410. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2021.104410. Epub 2021 Dec 17. J Proteomics. 2022. PMID: 34923174
-
Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses of leaves from Clematis terniflora DC. under high level of ultraviolet-B irradiation followed by dark treatment.J Proteomics. 2017 Jan 6;150:323-340. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2016.10.001. Epub 2016 Oct 17. J Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 27765634
-
Enhanced metabolic process to indole alkaloids in Clematis terniflora DC. after exposure to high level of UV-B irradiation followed by the dark.BMC Plant Biol. 2016 Oct 24;16(1):231. doi: 10.1186/s12870-016-0920-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2016. PMID: 27776479 Free PMC article.
-
Terrestrial ecosystems, increased solar ultraviolet radiation, and interactions with other climate change factors.Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2007 Mar;6(3):252-66. doi: 10.1039/b700019g. Epub 2007 Feb 1. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2007. PMID: 17344961 Review.
-
Separate and combined responses to water deficit and UV-B radiation.Plant Sci. 2013 Dec;213:98-105. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2013.09.003. Epub 2013 Sep 7. Plant Sci. 2013. PMID: 24157212 Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering nutrient stress in plants: integrative insight from metabolomics and proteomics.Funct Integr Genomics. 2025 Feb 15;25(1):38. doi: 10.1007/s10142-025-01551-y. Funct Integr Genomics. 2025. PMID: 39955391 Review.
References
-
- Tao M.; Zhu W.; Han H.; Liu S.; Liu A.; Li S.; Fu H.; Tian J. Mitochondrial proteomic analysis reveals the regulation of energy metabolism and reactive oxygen species production in Clematis terniflora DC. leaves under high-level UV-B radiation followed by dark treatment. J. Proteomics 2022, 254, 104410.10.1016/j.jprot.2021.104410. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen R. Z.; Cui L.; Guo Y. J.; Rong Y. M.; Lu X. H.; Sun M. Y.; Zhang L.; Tian J. K. In vivo study of four preparative extracts of Clematis terniflora DC. for antinociceptive activity and anti-inflammatory activity in rat model of carrageenan-induced chronic non-bacterial prostatitis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 134, 1018–1023. 10.1016/j.jep.2011.01.004. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

