X-ray imaging of 30 year old wine grape wood reveals cumulative impacts of rootstocks on scion secondary growth and Ravaz index
- PMID: 36643757
- PMCID: PMC9832875
- DOI: 10.1093/hr/uhac226
X-ray imaging of 30 year old wine grape wood reveals cumulative impacts of rootstocks on scion secondary growth and Ravaz index
Abstract
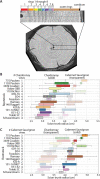
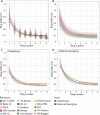
Annual rings from 30 year old vines in a California rootstock trial were measured to determine the effects of 15 different rootstocks on Chardonnay and Cabernet Sauvignon scions. Viticultural traits measuring vegetative growth, yield, berry quality, and nutrient uptake were collected at the beginning (1995 to 1999) and end (2017 to 2020) of the lifetime of a vineyard initially planted in 1991 and removed in 2021. X-ray Computed Tomography (CT) was used to measure ring widths in 103 vines. Ring width was modeled as a function of ring number using a negative exponential model. Early and late wood ring widths, cambium width, and scion trunk radius were correlated with 27 traits. Modeling of annual ring width shows that scions alter the width of the first rings but that rootstocks alter the decay of later rings, consistently shortening ring width throughout the lifetime of the vine. Ravaz index, juice pH, photosynthetic assimilation and transpiration rates, and instantaneous water use efficiency are correlated with scion trunk radius. Ultimately, our research indicates that rootstocks modulate secondary growth over years, altering physiology and agronomic traits. Rootstocks act in similar but distinct ways from climate to modulate ring width, which borrowing techniques from dendrochronology, can be used to monitor both genetic and environmental effects in woody perennial crop species.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nanjing Agricultural University.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Grapevine rootstocks affect growth-related scion phenotypes.Plant Direct. 2021 May 27;5(5):e00324. doi: 10.1002/pld3.324. eCollection 2021 May. Plant Direct. 2021. PMID: 34095741 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic assessment of how rootstock growth characteristics impact grafted tomato plant biomass, resource partitioning, yield, and fruit mineral composition.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Dec 15;13:948656. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.948656. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36589098 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of rootstocks on the growth and berry quality of Vitis vinifera cv. Cabernet Sauvignon grapevine in Changli zone, Hebei Province, China].Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2016 Jan;27(1):59-63. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2016. PMID: 27228593 Chinese.
-
Rootstocks: Diversity, Domestication, and Impacts on Shoot Phenotypes.Trends Plant Sci. 2016 May;21(5):418-437. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2015.11.008. Epub 2015 Dec 11. Trends Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 26698413 Review.
-
Grafting: A Technique to Modify Ion Accumulation in Horticultural Crops.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Oct 21;7:1457. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01457. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27818663 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abràmoff MD, Magalhães PJ, Ram SJ. Image processing with image. J Biophotonics international. 2004;11:36–42.
-
- Berstein Z, Fahn A. The effect of annual and bi-annual pruning on the seasonal changes in xylem formation in the grapevine: with five figures in the text. Ann Bot. 1960;24:159–71.
-
- Bravdo B, Hepner Y, Loinger Cet al. . Effect of crop level on growth, yield and wine quality of a high yielding Carignane vineyard. Am J Enol Vitic. 1984;35:247–52.
-
- Cheng J, Wei L, Mei Jet al. . Effect of rootstock on phenolic compounds and antioxidant properties in berries of grape (Vitis vinifera L.) cv. ‘Red Alexandria’. Sci Hortic. 2017;217:137–44.
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

