Fashionable, but What is Their Real Clinical Usefulness? NLR, LMR, and PLR as a Promising Indicator in Colorectal Cancer Prognosis: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 36643953
- PMCID: PMC9833126
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S391932
Fashionable, but What is Their Real Clinical Usefulness? NLR, LMR, and PLR as a Promising Indicator in Colorectal Cancer Prognosis: A Systematic Review
Abstract
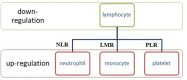
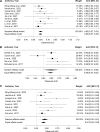
The link between inflammation and cancer is still an attractive subject of many studies because systemic inflammatory response has been proven to play a pivotal role in cancer progression and metastasis. The strongest relationship between chronic inflammation and cancer development is observed in colorectal cancer (CRC). The evaluation of ratios derived from the routinely performed inflammatory biomarkers shows limited performances and limited clinical utility when individually used as prognostic factors for patients with CRC. In this review, we would like to summarize the latest knowledge about the diagnostic utility of systemic inflammatory ratios: neutrophil/lymphocyte (NLR), lymphocyte/monocyte (LMR), and platelet/lymphocyte (PLR) in CRC. We focused on the papers that assessed the diagnostic utility of blood cell parameters on the basis of the area under the ROC curve published in the recent 6 years. Identification of biomarkers that are significantly associated with prognostic in cancer would help the selection of patients with a high risk of poor outcomes.
Keywords: biomarkers; colorectal cancer; inflammation; prognosis.
© 2023 Misiewicz and Dymicka-Piekarska.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that there is no possible conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wojciechowska U, Didkowska J. Nowotwory Złośliwe w Polsce w 2018 [Malignant tumors in Poland in 2018]. Krajowy Rejestr Nowotworów; 2020.
-
- Praktyce OW, Zyśk R, Wysocki P, Wyrwicz L. Colorectal cancer — the social significance of changes in the epidemiology and treatment options in Poland. Oncol Clin Pract. 2014;10(4):212–223.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

