Colchicine reduces atherosclerotic plaque vulnerability in rabbits
- PMID: 36643998
- PMCID: PMC9833268
- DOI: 10.1016/j.athplu.2021.08.008
Colchicine reduces atherosclerotic plaque vulnerability in rabbits
Abstract
Background and aims: The anti-inflammatory agent colchicine is gaining interest as a treatment for coronary artery disease. However, the effects of colchicine in atherosclerotic animal models are mostly unknown. This study aimed to evaluate colchicine in a rabbit model of atherosclerosis.
Methods: Twenty-two rabbits were fed a 0.5% cholesterol-enriched diet for 10 weeks and then randomized to receive either oral saline (n=11) or colchicine (350 μg/kg/day; n=11) for 6 weeks, with 0.2% cholesterol-diet during the treatment period. We performed intravascular ultrasound imaging (at start and end of treatment) and histology analyses of the descending thoracic aorta. Leucocyte activation was assessed in vitro on blood samples obtained during treatment.
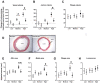
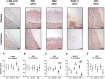
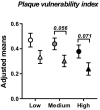
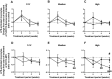
Results: Colchicine prevented positive aortic vascular remodelling (p=0.029 vs placebo). This effect was even more marked at high plasma cholesterol level (third quartile of plasma cholesterol, p=0.020). At high cholesterol level, both atherosclerotic plaque and media areas on histomorphology were reduced by colchicine compared to placebo (p=0.031 and p=0.039, respectively). Plaque fibrosis and macrophage area were reduced by colchicine (Masson's trichrome stain: p=0.038; RAM-11: p=0.026). The plaque vulnerability index, assessed by histology, was reduced by colchicine (p=0.040). Elastin/type I collagen ratio in media was significantly higher with colchicine compared to placebo (p=0.013). At a high level of plasma cholesterol, in vitro LPS challenge revealed a decrease in monocyte activation following treatment with colchicine (p<0.001) and no change in the placebo group (p=0.353).
Conclusions: Colchicine decreases plaque vulnerability with reductions in plaque inflammation, medial fibrosis, outward vascular remodelling and ex vivo monocyte activation.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Colchicine; Inflammation; Monocyte activation; Plaque vulnerability; Vascular remodelling.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Dr. Tardif reports receiving grant support from Amarin, Esperion, Ionis PharmaceuticalsIonis Pharmaceuticals and RegenXBio, receiving grant support and honoraria from AstraZeneca, Pfizer and Sanofi, receiving grant support and honoraria from and having minor equity interest in DalCor PharmaceuticalsDalCor Pharmaceuticals, holding a pending patent (US20170233812A1) on genetic markers for predicting responsiveness to therapy with a high-density lipoprotein (HDL)–raising or HDL mimicking agent, and holding pending patents (62/935,751 and 62/935,865) on methods for using low-dose colchicine after myocardial infarction, licensed to Montreal Heart Institute (Dr. Tardif has waived his rights in colchicine patents and does not stand to gain financially).
Figures


References
-
- Pfisterer M.E., Zellweger M.J., Gersh B.J. Management of stable coronary artery disease. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2010;375(9716):763–772. - PubMed
-
- Smith S.C., Benjamin E.J., Bonow R.O., Braun L.T., Creager M.A., Franklin B.A., et al. AHA/ACCF secondary prevention and risk reduction therapy for patients with coronary and other atherosclerotic vascular disease: 2011 update: a guideline from the American Heart Association and American College of Cardiology Foundation endorsed by the World Heart Federation and the Preventive Cardiovascular Nurses Association. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58(23):2432–2446. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin E.J., Blaha M.J., Chiuve S.E., Cushman M., Das S.R., Deo R., et al. American heart association statistics committee and stroke statistics subcommittee, heart disease and stroke statistics-2017 update: a report from the American heart association. Circulation. 2017;135(10) e146–e603. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ross R. Atherosclerosis--an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med. 1999;340(2):115–126. - PubMed
-
- Khan R., Spagnoli V., Tardif J.-C., L'Allier P.L. Novel anti-inflammatory therapies for the treatment of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 2015;240(2):497–509. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
