Role of Gut Microbiome in Cardiovascular Events: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 36644080
- PMCID: PMC9835843
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.32465
Role of Gut Microbiome in Cardiovascular Events: A Systematic Review
Abstract
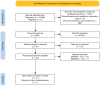
The gut microbiome helps maintain homeostasis in the body, but what if the gut experiences imbalance? It would lead to dysbiosis - which is involved in multiple diseases, including but not limited to cardiovascular diseases, the most common cause of mortality around the globe. This research paper aims to explain all the possible mechanisms known linking the gut microbiome to the contribution of worsening cardiovascular events. PubMed and Google Scholar were thoroughly explored to learn the role of the gut microbiome in cardiovascular events. A systematic review was performed using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines to analyze the possible pathways and the metabolites included in the study. Thirteen review articles were selected based on the assessment of multiple systematic reviews (AMSTAR) and the scale for the assessment of non-systematic review articles (SANRA) checklist scores. In this article, we have discussed the role of the gut microbiome in atherosclerosis, hypertension, metabolic disorders such as diabetes and obesity, coronary artery disease, etc. Various pathways to modify the gut microbiome are also discussed, along with the use of probiotics. Finally, we discussed the role of trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), a gut microbiome metabolite, as a biomarker for the prognosis of various diseases. This study concluded that the gut microbiome does play a crucial role in the worsening of cardiovascular diseases and the metabolites of which can be used as biomarkers in the prognosis of cardiovascular events.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; bacteria in the intestines; bacteroidetes; cardiovascular disease; cardiovascular events; firmicutes; gastrointestinal flora; gut microbiome; gut microbiota; myocardial infarction.
Copyright © 2022, Mansuri et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Understanding the Role of the Gut Microbiome in Diabetes and Therapeutics Targeting Leaky Gut: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2023 Jul 8;15(7):e41559. doi: 10.7759/cureus.41559. eCollection 2023 Jul. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37554593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel insights in the relationship of gut microbiota and coronary artery diseases.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022;62(14):3738-3750. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1868397. Epub 2021 Jan 5. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022. PMID: 33399007 Review.
-
Gut microbiota in coronary artery disease: a friend or foe?Biosci Rep. 2020 May 29;40(5):BSR20200454. doi: 10.1042/BSR20200454. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32352513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut Microbial Taxonomy and Its Role as a Biomarker in Aortic Diseases: A Systematic Review and Future Perspectives.J Clin Med. 2024 Nov 18;13(22):6938. doi: 10.3390/jcm13226938. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39598083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Gut Microbiome in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2023 Aug 21;15(8):e43862. doi: 10.7759/cureus.43862. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37614827 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The gut-heart axis: a review of gut microbiota, dysbiosis, and cardiovascular disease development.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025 Jan 9;87(1):177-191. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000002789. eCollection 2025 Jan. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40109640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Might Gut Microbiota Be a Target for a Personalized Therapeutic Approach in Patients Affected by Atherosclerosis Disease?J Pers Med. 2023 Sep 7;13(9):1360. doi: 10.3390/jpm13091360. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37763128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Promising Role of Probiotics in the Prevention of Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Their Implication in Reducing Coronary Artery Disease: A Literature Review.Cureus. 2025 Jun 18;17(6):e86292. doi: 10.7759/cureus.86292. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40535952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From multi-omics approaches to personalized medicine in myocardial infarction.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Oct 30;10:1250340. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1250340. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37965091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut Microbiota Perturbation in Early Life Could Influence Pediatric Blood Pressure Regulation in a Sex-Dependent Manner in Juvenile Rats.Nutrients. 2023 Jun 7;15(12):2661. doi: 10.3390/nu15122661. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37375565 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Impact of human microbiome on health. Das S, Khanna C, Singh S, Nandi S, Verma R. Microbial Diversity, Interventions and Scope. 2020:349–373.
-
- Mortality in the United States, 2018. Xu J, Murphy SL, Kochanek KD, Arias E. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/databriefs/db355-h.pdf NCHS data brief. 2018:8. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
