Public Knowledge, Awareness, Attitudes, and Practices Regarding Seizure Attacks Among People of Makkah City
- PMID: 36644092
- PMCID: PMC9836322
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.32485
Public Knowledge, Awareness, Attitudes, and Practices Regarding Seizure Attacks Among People of Makkah City
Abstract
Objectives: Seizures can occur as a result of a variety of health issues. Epilepsy is a common neurological disease and it is the most prevalent cause of seizures. Epileptic patients might experience a seizure attack at any moment. The aim of this study is to assess public knowledge, awareness, attitudes, and practices toward seizure attacks among residents of Makkah city.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted utilizing an online questionnaire, which was distributed through various social media platforms. The questionnaire consisted of five parts, taking sociodemographic characteristics into consideration, and evaluating knowledge, awareness, attitudes, and practices among the general population of Makkah city.
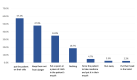
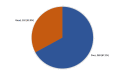
Results: A total of 401 participants completed the study questionnaire: 280 (69.8%) participants were females and 121 (30.2%) were males. Overall knowledge regarding epilepsy among the study participants was evaluated. A total of 132 (32.9%) participants had a good level of knowledge, while 269 (67.1%) exhibited poor knowledge. In addition, students had significantly better knowledge (44.7%) than individuals who were employed, retired, or unemployed (27.7%), (P=.004). Furthermore, participants who had previously heard about epilepsy were more knowledgeable (34.3%) than those who had not (P =.041). Additionally, participants who attended a course on seizure control (46.7%) had significantly better knowledge than those who did not (31.2%), (P=.037).
Conclusion: This study revealed that most of our sample of Makkah city residents had poor overall knowledge of epilepsy and seizure attacks. A health education program and awareness campaigns could help improve this lack of knowledge in Makkah city.
Keywords: attitudes; awareness; epilepsy; knowledge; makkah; seizure.
Copyright © 2022, Tawakul et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Seizures and epilepsy: an overview for neuroscientists. Stafstrom CE, Carmant L. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4448698/ Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2015;5:0. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Public awareness, attitudes, and first-aid measures on epilepsy in Tehran. Abbasi Kangevari M, Kolahi AA, Farsar AR, Kermaniranjbar S. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30598677/ Iran J Child Neurol. 2019;13:91–106. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Public knowledge and attitudes towards epilepsy in Jordan. Daoud A, Al-Safi S, Otoom S, Wahba L, Alkofahi A. Seizure. 2007;16:521–526. - PubMed
-
- Jackie Aker. Epilepsy Foundation Puts the Brain Front and Center to Rally Everyone to End Epilepsy. Epilepsy Foundation. [ Jun; 2022 ]. 2018. https://www.epilepsy.com/stories/epilepsy-foundation-puts-brain-front-an... https://www.epilepsy.com/stories/epilepsy-foundation-puts-brain-front-an...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources