FTY720 Attenuates LPS-Induced Inflammatory Bone Loss by Inhibiting Osteoclastogenesis via the NF- κ B and HDAC4/ATF Pathways
- PMID: 36644540
- PMCID: PMC9839404
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/8571649
FTY720 Attenuates LPS-Induced Inflammatory Bone Loss by Inhibiting Osteoclastogenesis via the NF- κ B and HDAC4/ATF Pathways
Abstract
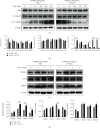
Osteoclast (OC) abnormalities lead to many osteolytic diseases, such as osteoporosis, inflammatory bone erosion, and tumor-induced osteolysis. Exploring effective strategies to remediate OCs dysregulation is essential. FTY720, also known as fingolimod, has been approved for the treatment of multiple sclerosis and has anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects. Here, we found that FTY720 inhibited osteoclastogenesis and OC function by inhibiting nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) signaling. Interestingly, we also found that FTY720 inhibited osteoclastogenesis by upregulating histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4) expression levels and downregulating activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) expression levels. In vivo, FTY720 treatment prevented lipopolysaccharide- (LPS-) induced calvarial osteolysis and significantly reduced the number of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase- (TRAP-) positive OCs. Taken together, these results demonstrate that FTY720 can inhibit osteoclastogenesis and ameliorate inflammation-induced bone loss. Which may provide evidence of a new therapeutic target for skeletal diseases caused by OC abnormalities.
Copyright © 2023 Chongwei Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

