High throughput screening for drugs that inhibit 3C-like protease in SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 36646172
- PMCID: PMC9839384
- DOI: 10.1016/j.slasd.2023.01.001
High throughput screening for drugs that inhibit 3C-like protease in SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
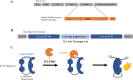
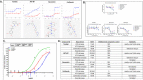
The SARS coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic remains a major problem in many parts of the world and infection rates remain at extremely high levels. This high prevalence drives the continued emergence of new variants, and possibly ones that are more vaccine-resistant and that can drive infections even in highly vaccinated populations. The high rate of variant evolution makes clear the need for new therapeutics that can be clinically applied to minimize or eliminate the effects of COVID-19. With a hurdle of 10 years, on average, for first in class small molecule therapeutics to achieve FDA approval, the fastest way to identify therapeutics is by drug repurposing. To this end, we developed a high throughput cell-based screen that incorporates the essential viral 3C-like protease and its peptide cleavage site into a luciferase complementation assay to evaluate the efficacy of known drugs encompassing approximately 15,000 clinical-stage or FDA-approved small molecules. Confirmed inhibitors were also tested to determine their cytotoxic properties. Medicinal chemistry efforts to optimize the hits identified Tranilast as a potential lead. Here, we report the rapid screening and identification of potentially relevant drugs that exhibit selective inhibition of the SARS-CoV-2 viral 3C-like protease.
Keywords: 3CL-PRO; COVID-19; Cell-based; HTS; M-PRO; PL-PRO.
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declared no potential conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship and or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development of a Fluorescence-Based, High-Throughput SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Reporter Assay.J Virol. 2020 Oct 27;94(22):e01265-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01265-20. Print 2020 Oct 27. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32843534 Free PMC article.
-
High-Throughput Screening for Drugs That Inhibit Papain-Like Protease in SARS-CoV-2.SLAS Discov. 2020 Dec;25(10):1152-1161. doi: 10.1177/2472555220963667. Epub 2020 Oct 10. SLAS Discov. 2020. PMID: 33043784 Free PMC article.
-
Novel dithiocarbamates selectively inhibit 3CL protease of SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses.Eur J Med Chem. 2023 Mar 15;250:115186. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115186. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Eur J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36796300 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Mpro: A Potential Target for Peptidomimetics and Small-Molecule Inhibitors.Biomolecules. 2021 Apr 19;11(4):607. doi: 10.3390/biom11040607. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33921886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design and Evaluation of Anti-SARS-Coronavirus Agents Based on Molecular Interactions with the Viral Protease.Molecules. 2020 Aug 27;25(17):3920. doi: 10.3390/molecules25173920. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32867349 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phytochemicals: Promising Inhibitors of Human Rhinovirus Type 14 3C Protease as a Strategy to Fight the Common Cold.Curr Top Med Chem. 2024;24(15):1343-1358. doi: 10.2174/0115680266308561240427065854. Curr Top Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38698747
-
Yeast-Based Screening of Anti-Viral Molecules.Microorganisms. 2024 Mar 14;12(3):578. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12030578. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38543629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor identification using a cellular gain-of-signal assay for high-throughput screening.SLAS Discov. 2024 Sep;29(6):100181. doi: 10.1016/j.slasd.2024.100181. Epub 2024 Aug 22. SLAS Discov. 2024. PMID: 39173830 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease (Mpro) as Anti-Coronavirus Agents.Biomolecules. 2024 Jul 4;14(7):797. doi: 10.3390/biom14070797. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A high-throughput cell-based screening method for Zika virus protease inhibitor discovery.SLAS Discov. 2024 Jul;29(5):100164. doi: 10.1016/j.slasd.2024.100164. Epub 2024 May 24. SLAS Discov. 2024. PMID: 38796112 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jin Z., Du X., Xu Y., et al. Structure of M(pro) from SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of its inhibitors. Nature. 2020;582:289–293. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

