Effect of combination fluoxetine and exercise on prefrontal BDNF, anxiety-like behavior and fear extinction in a female rat model of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD): a comparison with male animals
- PMID: 36647145
- PMCID: PMC9843848
- DOI: 10.1186/s12993-023-00204-z
Effect of combination fluoxetine and exercise on prefrontal BDNF, anxiety-like behavior and fear extinction in a female rat model of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD): a comparison with male animals
Abstract
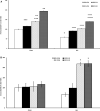
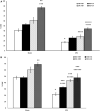
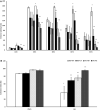
Despite significant differences between men and women in the symptoms of PTSD and the response to therapeutic interventions, most PTSD studies have been done on male subjects. Continuing our previous study in male rats, this study aimed at better understanding the effect of a combination therapy of exercise with fluoxetine on female PTSD rats. The results were then compared with our past findings in male animals. Female adult Wistar rats subjected to PTSD were treated with moderate treadmill exercise or fluoxetine, or a combination of both. PTSD was induced by the single prolonged stress (SPS) model. Elevated plus-maze (EPM), serum and prefrontal BDNF, and fear extinctions were evaluated. The results showed that exercise plus fluoxetine decreased anxiety-like behavior, improved fear extinction, and increased BDNF changes in female rats. The effects of exercise alone were comparable with those of combination therapy except that combination therapy was more effective on OAT (open arm entry). The majority of results in female rats, except for those of prefrontal BDNF, 4th extinction, and OAT, were similar to those of male rats as shown in our previous study. According to our findings, exercise as a safe and cost-effective intervention can be considered as a complementary efficient option for PTSD treatment in both sexes. To achieve better treatment outcomes in PTSD patient, considering sex differences is recommended.
Keywords: Exercise; Fluoxetine; PTSD; Single prolonged stress; sex.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose that could influence this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of moderate treadmill exercise and fluoxetine on behavioural and cognitive deficits, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysfunction and alternations in hippocampal BDNF and mRNA expression of apoptosis - related proteins in a rat model of post-traumatic stress disorder.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2017 Mar;139:165-178. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2017.01.009. Epub 2017 Jan 28. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2017. PMID: 28137660
-
Effect of treadmill exercise on serum corticosterone, serum and hippocampal BDNF, hippocampal apoptosis and anxiety behavior in an ovariectomized rat model of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).Physiol Behav. 2022 Jan 1;243:113629. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2021.113629. Epub 2021 Oct 29. Physiol Behav. 2022. PMID: 34743976
-
Combined brain-derived neurotrophic factor with extinction training alleviate impaired fear extinction in an animal model of post-traumatic stress disorder.Genes Brain Behav. 2019 Sep;18(7):e12520. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12520. Epub 2018 Oct 9. Genes Brain Behav. 2019. PMID: 30246290
-
Interaction of Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor, Exercise, and Fear Extinction: Implications for Post-traumatic Stress Disorder.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024;22(4):543-556. doi: 10.2174/1570159X21666230724101321. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37491857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fear extinction and BDNF: translating animal models of PTSD to the clinic.Genes Brain Behav. 2012 Jul;11(5):503-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2012.00801.x. Epub 2012 May 11. Genes Brain Behav. 2012. PMID: 22530815 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Low emotional contagious behavior induces PTSD susceptibility in observers and is related to the regulation of oxytocin receptor in mice.Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2025 Apr;25(2):515-530. doi: 10.3758/s13415-024-01244-2. Epub 2025 Jan 22. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39843825
-
New Insights into Contradictory Changes in Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) in Rodent Models of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD).Neurochem Res. 2024 Dec;49(12):3226-3243. doi: 10.1007/s11064-024-04242-5. Epub 2024 Sep 16. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 39283581 Review.
-
Fluoxetine Rescues Excessive Myelin Formation and Psychological Behaviors in a Murine PTSD Model.Neurosci Bull. 2024 Aug;40(8):1037-1052. doi: 10.1007/s12264-024-01249-4. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Neurosci Bull. 2024. PMID: 39014176 Free PMC article.
-
Is There a Natural, Non-addictive, and Non-anti-reward, Safe, Gene-based Solution to Treat Reward Deficiency Syndrome? KB220 Variants vs GLP-1 Analogs.J Addict Psychiatry. 2024;8(1):34-49. Epub 2024 May 20. J Addict Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39618491 Free PMC article.
-
Estrous cycle stage gates the effect of stress on reward learning.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2025 Jul 16. doi: 10.1038/s41386-025-02170-8. Online ahead of print. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40670622
References
-
- Mazor A, Matar MA, Kaplan Z, Kozlovsky N, Zohar J, Cohen H. Gender-related qualitative differences in baseline and post-stress anxiety responses are not reflected in the incidence of criterion-based PTSD-like behaviour patterns. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2009;10(4–3):856–869. doi: 10.1080/15622970701561383. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

