Evaluation of diagnostic time in pediatric patients with eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders according to their clinical features
- PMID: 36647148
- PMCID: PMC9841131
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-023-01410-1
Evaluation of diagnostic time in pediatric patients with eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders according to their clinical features
Abstract
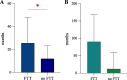
Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGIDs) are chronic/remittent inflammatory diseases associated with a substantial diagnostic delay, often attributable to misdiagnosis and variable clinical presentation in adults. In the pediatric population, few studies have been conducted worldwide reporting EGID diagnostic delay and its consequences on patients. This study aims to analyze and identify potential clinical factors and complications associated with a longer diagnostic time. We performed a retrospective analysis of pediatric patients with EGIDs followed at the Center for Pediatric EGIDs in Pavia, Italy. A total of 60 patients with EGIDs were enrolled. Thirty-nine (65%) patients had EoE, and 21 (35%) non-esophageal EGIDs. EGID diagnosis was achieved about 2 years after the symptom onset, and the median diagnostic time was 12 months (IQR 12-24 months). Diagnostic time was 12 months (IQR 12-69) in non-esophageal EGIDs and 12 months (IQR 4-24 months) in EoE patients. EoE patients presenting with FTT and feeding issues experienced a longer diagnostic time (p = 0.02 and p = 0.05, respectively) than children without growth and feeding impairments.In this study, symptoms appeared about 2 years before the definitive EGID diagnosis was reached, and this diagnostic time was shorter than the delay observed in other published studies. Especially in EoE children, the diagnostic time is significantly associated with impaired child growth, highlighting the importance of an early diagnosis to prevent esophageal stenosis and failure to thrive.
Keywords: Adolescents; Children; Diagnostic time; Eosinophilic esophagitis; Failure to thrive; Growth; Non-esophageal eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

