Comparative analysis of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells and the cognate umbilical cord mesenchymal stem/stromal cells
- PMID: 36647346
- PMCID: PMC9840238
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12683
Comparative analysis of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells and the cognate umbilical cord mesenchymal stem/stromal cells
Abstract
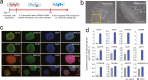
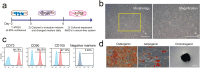
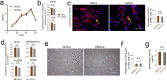
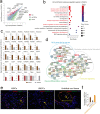
Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs) show tremendous potential for regenerative medicine due to their self-renewal, multi-differentiation and immunomodulatory capabilities. Largely studies had indicated conventional tissue-derived MSCs have considerable limited expandability and donor variability which hinders further application. Induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSCs)-derived MSCs (iMSCs) have created exciting source for standardized cellular therapy. However, the cellular and molecular differences between iMSCs and the cognate tissue-derived MSCs remains poorly explored. In this study, we first successfully reprogrammed human umbilical cords-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (UMSCs) into iPSCs by using the cocktails of mRNA. Subsequently, iPSCs were further differentiated into iMSCs in xeno-free induction medium. Then, iMSCs were compared with the donor matched UMSCs by assessing proliferative state, differentiation capability, immunomodulatory potential through immunohistochemical analysis, flow cytometric analysis, transcriptome sequencing analysis, and combine with coculture with immune cell population. The results showed that iMSCs exhibited high expression of MSCs positive-makers CD73, CD90, CD105 and lack expression of negative-maker cocktails CD34, CD45, CD11b, CD19, HLA-DR; also successfully differentiated into osteocytes, chondrocytes and adipocytes. Further, the iMSCs were similar with their parental UMSCs in cell proliferative state detected by the CCK-8 assay, and in cell rejuvenation state assessed by β-Galactosidase staining and telomerase activity related mRNA and protein analysis. However, iMSCs exhibited similarity to resident MSCs in Homeobox (Hox) genes expression profile and presented better neural differentiation potential by activation of NESTIN related pathway. Moreover, iMSCs owned enhanced immunosuppression capacity through downregulation pools of pro-inflammatory factors, including IL6, IL1B etc. and upregulation anti-inflammatory factors NOS1, TGFB etc. signals. In summary, our study provides an attractive cell source for basic research and offers fundamental biological insight of iMSCs-based therapy.
Keywords: Immunomodulatory; Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs); Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs); Transcriptomics; iPSC-derived MSCs (iMSCs).
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative analysis of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells and umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Sep;25(18):8904-8919. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16851. Epub 2021 Aug 13. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34390186 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of canine induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Comparison of differentiation strategies and cell origins.Regen Ther. 2025 May 29;30:112-122. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2025.05.008. eCollection 2025 Dec. Regen Ther. 2025. PMID: 40511257 Free PMC article.
-
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Are Functionally and Genetically Different From Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells.Stem Cells. 2019 Jun;37(6):754-765. doi: 10.1002/stem.2993. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Stem Cells. 2019. PMID: 30779868 Free PMC article.
-
hiPSC-derived iMSCs: NextGen MSCs as an advanced therapeutically active cell resource for regenerative medicine.J Cell Mol Med. 2016 Aug;20(8):1571-88. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12839. Epub 2016 Apr 21. J Cell Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27097531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methods to produce induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Mesenchymal stem cells from induced pluripotent stem cells.World J Stem Cells. 2021 Aug 26;13(8):1094-1111. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i8.1094. World J Stem Cells. 2021. PMID: 34567428 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulatory T lymphocytes as a treatment method for rheumatoid arthritis - Superiority of allogeneic to autologous cells.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 30;10(17):e36512. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36512. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39319132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in therapies using mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes for treatment of peripheral nerve injury: state of the art and future perspectives.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Nov 1;20(11):3151-3171. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-00235. Epub 2024 Oct 22. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 39435603 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies in product engineering of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: unveiling the mechanisms underpinning the promotive effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 May 2;12:1363780. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1363780. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38756412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The influence of cell source on the senescence of human mesenchymal stem/stromal cells.Hum Cell. 2025 Apr 12;38(3):87. doi: 10.1007/s13577-025-01213-y. Hum Cell. 2025. PMID: 40221541 Review.
-
Advancements and Innovative Strategies in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy: A Comprehensive Review.Stem Cells Int. 2024 Sep 30;2024:4073485. doi: 10.1155/2024/4073485. eCollection 2024. Stem Cells Int. 2024. PMID: 39377039 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Montesinos J.J., Flores-Figueroa E., Castillo-Medina S., Flores-Guzmán P., Hernández-Estévez E., Fajardo-Orduña G., Orozco S., Mayani H. Human mesenchymal stromal cells from adult and neonatal sources: comparative analysis of their morphology, immunophenotype, differentiation patterns and neural protein expression. Cytotherapy. 2009;11:163–176. doi: 10.1080/14653240802582075. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

