Knowledge and Awareness of Non-Technical Skills Over the Course of an Educational Program in Nursing - A Repeated Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 36647513
- PMCID: PMC9840371
- DOI: 10.2147/AMEP.S379341
Knowledge and Awareness of Non-Technical Skills Over the Course of an Educational Program in Nursing - A Repeated Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
Background: Non-technical skills (NTS) play an important role in preventing adverse events during hospitalization. Knowledge, awareness and mastery of NTS becomes important key factors in preventing errors. Current status of students and supervisor's knowledge and awareness of NTS are needed in order to construct an educational plan for improvement.
Purpose: To examine knowledge and awareness of NTS over the course of continuing education of nurse anaesthetists, emergency care nurses, critical care nurses, and operating room nurses.
Methods: A descriptive, repetitive cross-sectional design with a questionnaire was used to evaluate knowledge and awareness in students and their supervisors about NTS at two different time points during the educational program. Cross tabulations were used in comparisons across specialties and between students and supervisors, frequencies to identify the levels of self-reported knowledge/importance/focus in clinical practice/ impact on adverse events.
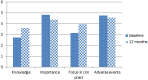
Results: The results showed that there was a numeric difference between the reported knowledge/focus in clinical practice on the one hand and importance/ impact on adverse events on the other, and that this gap was reduced after 12 months of education with special focus on NTS. There was no difference across specialties. Supervisors had higher focus on NTS in clinical practice and on the impact on adverse events, than students at both measurements.
Conclusion: These data suggest that NTS may have important potential for improvement if included into learning programs both in education and clinical practice. Integration of NTS in various learning activities seems to strengthen students' competence about NTS.
Keywords: NTS; non-technical skills; nursing education; patient safety.
© 2023 Wevling et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors in the present study claim no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Student and educator experiences of maternal-child simulation-based learning: a systematic review of qualitative evidence protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Jan;13(1):14-26. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-1694. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26447004
-
Development of non-technical skills through virtual patients for undergraduate nursing students: An exploratory study.Nurse Educ Today. 2019 Feb;73:94-101. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2018.11.008. Epub 2018 Nov 14. Nurse Educ Today. 2019. PMID: 30610960
-
The evaluation of a framework for measuring the non-technical ward round skills of final year nursing students: An observational study.Nurse Educ Today. 2016 Oct;45:87-90. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2016.06.024. Epub 2016 Jul 12. Nurse Educ Today. 2016. PMID: 27429411
-
Developing a novel framework for non-technical skills learning strategies for undergraduates: A systematic review.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2018 Oct 9;36:29-40. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2018.10.005. eCollection 2018 Dec. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2018. PMID: 30370054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence-informed practice versus evidence-based practice educational interventions for improving knowledge, attitudes, understanding, and behavior toward the application of evidence into practice: A comprehensive systematic review of UG student.Campbell Syst Rev. 2022 Apr 16;18(2):e1233. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1233. eCollection 2022 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36911346 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The pedagogical liminality of patient and public involvement in initial healthcare professional education: an umbrella review.Res Involv Engagem. 2025 May 19;11(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s40900-025-00704-4. Res Involv Engagem. 2025. PMID: 40390072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of an Order-Assist Mobile Application on Pediatric Anesthesia Safety: An Observational Study.Children (Basel). 2023 Nov 27;10(12):1860. doi: 10.3390/children10121860. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136062 Free PMC article.
-
An integrated communication and technical skills educational intervention in critical healthcare situations: A qualitative method.Nurs Open. 2025 Feb;12(2):e70002. doi: 10.1002/nop2.70002. Nurs Open. 2025. PMID: 39945361 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Clinical Experience in Advanced Practice Nursing Education-A Cross-Sectional Study of Norwegian Advanced Practice Nurses' Perspectives.Nurs Rep. 2023 Sep 13;13(3):1304-1317. doi: 10.3390/nursrep13030110. Nurs Rep. 2023. PMID: 37755353 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous