Microinjection in C. elegans by direct penetration of elastomeric membranes
- PMID: 36647539
- PMCID: PMC9840533
- DOI: 10.1063/5.0130806
Microinjection in C. elegans by direct penetration of elastomeric membranes
Abstract
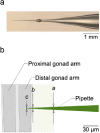
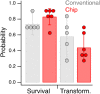
The nematode worm C. elegans is widely used in basic and translational research. The creation of transgenic strains by injecting DNA constructs into the worm's gonad is an essential step in many C. elegans research projects. This paper describes the fabrication and use of a minimalist microfluidic chip for performing microinjections. The worm is immobilized in a tight-fitting microchannel, one sidewall of which is a thin elastomeric membrane through which the injection pipet penetrates to reach the worm. The pipet is neither broken nor clogged by passing through the membrane, and the membrane reseals when the pipet is withdrawn. Rates of survival and transgenesis are similar to those in the conventional method. Novice users found injections using the device easier to learn than the conventional method. The principle of direct penetration of elastomeric membranes is adaptable to microinjections in a wide range of organisms including cells, embryos, and other small animal models. It could, therefore, lead to a new generation of microinjection systems for basic, translational, and industrial applications.
© 2023 Author(s).
Figures




Similar articles
-
Microfluidic Device for Microinjection of Caenorhabditis elegans.Micromachines (Basel). 2020 Mar 11;11(3):295. doi: 10.3390/mi11030295. Micromachines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32168862 Free PMC article.
-
A simple method to dramatically increase C. elegans germline microinjection efficiency.Dev Biol. 2023 Oct;502:63-67. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2023.07.003. Epub 2023 Jul 9. Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37433390 Free PMC article.
-
A microfluidic device for automated, high-speed microinjection of Caenorhabditis elegans.Biomicrofluidics. 2016 Feb 26;10(1):011912. doi: 10.1063/1.4941984. eCollection 2016 Jan. Biomicrofluidics. 2016. PMID: 26958099 Free PMC article.
-
[A worm's life].Med Sci (Paris). 2003 Dec;19(12):1209-17. doi: 10.1051/medsci/200319121209. Med Sci (Paris). 2003. PMID: 14691745 Review. French.
-
Microfluidic systems for high-throughput and high-content screening using the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans.Lab Chip. 2017 Nov 7;17(22):3736-3759. doi: 10.1039/c7lc00509a. Lab Chip. 2017. PMID: 28840220 Review.
Cited by
-
3D nanoprinting of embryo microinjection needles with anti-clogging features.Microsyst Nanoeng. 2025 Sep 11;11(1):171. doi: 10.1038/s41378-025-01005-2. Microsyst Nanoeng. 2025. PMID: 40935820 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
