PRIMPOL competes with RAD51 to resolve G-quadruplex-induced replication stress via its interaction with RPA
- PMID: 36647718
- PMCID: PMC10160237
- DOI: 10.3724/abbs.2022165
PRIMPOL competes with RAD51 to resolve G-quadruplex-induced replication stress via its interaction with RPA
Abstract
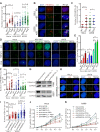
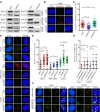
PRIMPOL (primase-polymerase) is a recently discovered DNA primase-polymerase involved in DNA damage tolerance and replication stress response in eukaryotic cells. However, the detailed mechanism of the PRIMPOL response to replication stress remains elusive. Here, we demonstrate that replication-related factors, including replication protein A (RPA), regulate the accumulation of PRIMPOL in subnuclear foci in response to replication stress induced by replication inhibitors. Moreover, PRIMPOL works at G-quadruplexes (G4s) in human cells to resolve the replication stress induced by G4s. The formation of PRIMPOL foci persists throughout the cell cycle. We further demonstrate that PRIMPOL competes with RAD51 to resolve G4-induced replication stress. In conclusion, our results provide novel insight into the mechanism of PRIMPOL in G4s to resolve replication stress and competition between PRIMPOL (repriming)- and RAD51 (fork reversal)-mediated pathways, which indicates a new strategy to improve the tumor response to DNA-damaging chemotherapy by targeting the PRIMPOL pathway.
Keywords: G-quadruplex; PRIMPOL; RAD51; RPA; replication stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
DNA synthesis across DNA hairpins by human PrimPol.DNA Repair (Amst). 2024 Oct;142:103741. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2024.103741. Epub 2024 Aug 8. DNA Repair (Amst). 2024. PMID: 39153403
-
PrimPol Is Required for Replicative Tolerance of G Quadruplexes in Vertebrate Cells.Mol Cell. 2016 Jan 7;61(1):161-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.10.038. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 26626482 Free PMC article.
-
PRIMPOL ready, set, reprime!Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2021 Feb;56(1):17-30. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2020.1841089. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33179522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human PrimPol activity is enhanced by RPA.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 10;7(1):783. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-00958-3. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28396594 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial DNA replication: a PrimPol perspective.Biochem Soc Trans. 2017 Apr 15;45(2):513-529. doi: 10.1042/BST20160162. Biochem Soc Trans. 2017. PMID: 28408491 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human CST complex restricts excessive PrimPol repriming upon UV induced replication stress by suppressing p21.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Apr 24;52(7):3778-3793. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae078. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38348929 Free PMC article.
-
DNA synthesis across DNA hairpins by human PrimPol.DNA Repair (Amst). 2024 Oct;142:103741. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2024.103741. Epub 2024 Aug 8. DNA Repair (Amst). 2024. PMID: 39153403
-
Role of Oxidative Stress in the Occurrence, Development, and Treatment of Breast Cancer.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jan 17;14(1):104. doi: 10.3390/antiox14010104. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39857438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accurate DNA Synthesis Across 8-Oxoadenine by Human PrimPol.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 16;26(14):6796. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146796. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725042 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Batista LF, Kaina B, Meneghini R, Menck CF. How DNA lesions are turned into powerful killing structures: insights from UV-induced apoptosis. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. . 2009;681:197–208. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2008.09.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Frasson I, Pirota V, Richter SN, Doria F. Multimeric G-quadruplexes: a review on their biological roles and targeting. Int J Biol Macromolecules. . 2022;204:89–102. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.01.197. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Panichnantakul P, Patel A, Tse EY, Wyatt HD. An open-source platform to quantify subnuclear foci and protein colocalization in response to replication stress. DNA Repair. . 2021;105:103156. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2021.103156. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

