Beyond adaptive immunity: induction of trained immunity by COVID-19 adenoviral vaccines
- PMID: 36647822
- PMCID: PMC9843054
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI166467
Beyond adaptive immunity: induction of trained immunity by COVID-19 adenoviral vaccines
Abstract
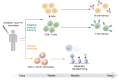
The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus, has resulted in much human suffering and societal disruption. The ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine against COVID-19 has had a crucial role in the fight against the pandemic. While ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 has been shown to induce adaptive B and T cell responses, which protect against COVID-19, in this issue of the JCI, Murphy et al. show that this vaccine also induces trained innate immunity. This finding contributes to a better understanding of the complex immunological effects of adenoviral-based vaccines, provides the possibility of clinically relevant heterologous effects of these vaccines, and suggests that other adenoviral-based vaccines may induce trained immunity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment on
- Trained immunity is induced in humans after immunization with an adenoviral vector COVID-19 vaccine
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

