Ten years of our translational research in the field of veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
- PMID: 36647905
- PMCID: PMC9906662
- DOI: 10.33549/physiolres.934999
Ten years of our translational research in the field of veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
Abstract
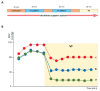
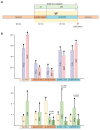
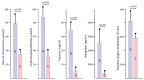
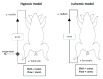
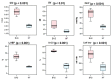
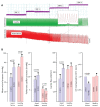
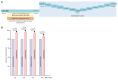
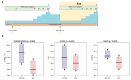
Extracorporeal life support is a treatment modality that provides prolonged blood circulation, gas exchange and can substitute functions of heart and lungs to provide urgent cardio-respiratory stabilization in patients with severe but potentially reversible cardiopulmonary failure refractory to conventional therapy. Generally, the therapy targets blood pressure, volume status, and end-organs perfusion. As there are significant differences in hemodynamic efficacy among different percutaneous circulatory support systems, it should be carefully considered when selecting the most appropriate circulatory support for specific medical conditions in individual patients. Despite severe metabolic and hemodynamic deterioration during prolonged cardiac arrest, venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA ECMO) can rapidly revert otherwise fatal prognosis, thus carrying a potential for improvement in survival rate, which can be even improved by introduction of mild therapeutic hypothermia. In order to allow a rapid transfer of knowledge to clinical medicine two porcine models were developed for studying efficiency of the VA ECMO in treatments of acute cardiogenic shock and progressive chronic heart failure. These models allowed also an intensive research of adverse events accompanying a clinical use of VA ECMO and their possible compensations. The results indicated that in order to weaken the negative effects of increased afterload on the left ventricular function the optimal VA ECMO flow in cardiogenic shock should be as low as possible to allow adequate tissue perfusion. The left ventricle can be also unloaded by an ECG-synchronized pulsatile flow if using a novel pulsatile ECMO system. Thus, pulsatility of VA ECMO flow may improve coronary perfusion even under conditions of high ECMO blood flows. And last but not least, also the percutaneous balloon atrial septostomy is a very perspective method how to passively decompress overloaded left heart.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Prevention and treatment of pulmonary congestion in patients undergoing venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for cardiogenic shock.Eur Heart J. 2020 Oct 7;41(38):3753-3761. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa547. Eur Heart J. 2020. PMID: 33099278
-
Atrial Septostomy for Left Ventricular Unloading During Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Cardiogenic Shock: Animal Model.JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2021 Dec 27;14(24):2698-2707. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2021.09.011. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2021. PMID: 34949394
-
Venoarterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Cardiogenic Shock and Cardiac Arrest.Circ Heart Fail. 2018 Sep;11(9):e004905. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.118.004905. Circ Heart Fail. 2018. PMID: 30354364 Review.
-
Clinical utility of venoarterial-extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA-ECMO) in patients with drug-induced cardiogenic shock: a retrospective study of the Extracorporeal Life Support Organizations' ECMO case registry.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2020 Jul;58(7):705-710. doi: 10.1080/15563650.2019.1676896. Epub 2019 Oct 16. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2020. PMID: 31617764
-
Left Ventricular Unloading During Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Patients With Cardiogenic Shock.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 Feb 19;73(6):654-662. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.10.085. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30765031
References
-
- Richardson AC, Tonna JE, Nanjayya V, Nixon P, Abrams D, Raman L, Bernard S, et al. Extracorporeal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in Adults. Interim Guideline Consensus Statement From the Extracorporeal Life Support Organization. ASAIO J. 2021;67:221–228. doi: 10.1097/MAT.0000000000001344. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- REGISTRY: Extracorporeal Life Support Registry Report. Available online: https://www.elso.org/Registry/Statistics/published January 30, 2020.
-
- Fredriksson M, Aune S, Bang A, Thoren AB, Lindqvist J, Karlsson T, Herlitz J. Cardiac arrest outside and inside hospital in a community: mechanisms behind the differences in outcome and outcome in relation to time of arrest. Am Heart J. 2010;159:749–756. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2010.01.015. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
