Gain-of-function variants in the ion channel gene TRPM3 underlie a spectrum of neurodevelopmental disorders
- PMID: 36648066
- PMCID: PMC9886277
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.81032
Gain-of-function variants in the ion channel gene TRPM3 underlie a spectrum of neurodevelopmental disorders
Abstract
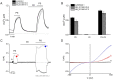
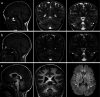
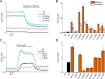
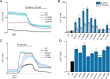
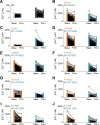
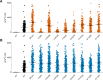
TRPM3 is a temperature- and neurosteroid-sensitive plasma membrane cation channel expressed in a variety of neuronal and non-neuronal cells. Recently, rare de novo variants in TRPM3 were identified in individuals with developmental and epileptic encephalopathy, but the link between TRPM3 activity and neuronal disease remains poorly understood. We previously reported that two disease-associated variants in TRPM3 lead to a gain of channel function . Here, we report a further 10 patients carrying one of seven additional heterozygous TRPM3 missense variants. These patients present with a broad spectrum of neurodevelopmental symptoms, including global developmental delay, intellectual disability, epilepsy, musculo-skeletal anomalies, and altered pain perception. We describe a cerebellar phenotype with ataxia or severe hypotonia, nystagmus, and cerebellar atrophy in more than half of the patients. All disease-associated variants exhibited a robust gain-of-function phenotype, characterized by increased basal activity leading to cellular calcium overload and by enhanced responses to the neurosteroid ligand pregnenolone sulfate when co-expressed with wild-type TRPM3 in mammalian cells. The antiseizure medication primidone, a known TRPM3 antagonist, reduced the increased basal activity of all mutant channels. These findings establish gain-of-function of TRPM3 as the cause of a spectrum of autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental disorders with frequent cerebellar involvement in humans and provide support for the evaluation of TRPM3 antagonists as a potential therapy.
Keywords: TRPM3; cell biology; cerebellar atrophy; epilepsy; gain-of-function; human; intellectual disability; neurodevelopment; neuroscience.
© 2023, Burglen, Van Hoeymissen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
LB, EV, LQ, MB, NB, FB, CD, KD, AD, MF, NF, CG, IH, KH, DH, AJ, AK, VN, CP, MR, AA, SZ, VR, SR, ST, SV, LV, TR, DR, DD, TV, JV No competing interests declared
Figures












References
-
- Aldinger KA, Thomson Z, Phelps IG, Haldipur P, Deng M, Timms AE, Hirano M, Santpere G, Roco C, Rosenberg AB, Lorente-Galdos B, Gulden FO, O’Day D, Overman LM, Lisgo SN, Alexandre P, Sestan N, Doherty D, Dobyns WB, Seelig G, Glass IA, Millen KJ. Spatial and cell type transcriptional landscape of human cerebellar development. Nature Neuroscience. 2021;24:1163–1175. doi: 10.1038/s41593-021-00872-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Behrendt M, Gruss F, Enzeroth R, Dembla S, Zhao S, Crassous PA, Mohr F, Nys M, Louros N, Gallardo R, Zorzini V, Wagner D, Economou A, Rousseau F, Schymkowitz J, Philipp SE, Rohacs T, Ulens C, Oberwinkler J. The structural basis for an on-off switch controlling Gβγ-mediated inhibition of TRPM3 channels. PNAS. 2020;117:29090–29100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2001177117. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dembla S, Behrendt M, Mohr F, Goecke C, Sondermann J, Schneider FM, Schmidt M, Stab J, Enzeroth R, Leitner MG, Nuñez-Badinez P, Schwenk J, Nürnberg B, Cohen A, Philipp SE, Greffrath W, Bünemann M, Oliver D, Zakharian E, Schmidt M, Oberwinkler J. Anti-Nociceptive action of peripheral mu-opioid receptors by G-beta-gamma protein-mediated inhibition of TRPM3 channels. eLife. 2017;6:e26280. doi: 10.7554/eLife.26280. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- de Sainte Agathe JM, Van-Gils J, Lasseaux E, Arveiler B, Lacombe D, Pfirrmann C, Raclet V, Gaston L, Plaisant C, Aupy J, Trimouille A. Confirmation and expansion of the phenotype associated with the recurrent p.val837met variant in TRPM3. European Journal of Medical Genetics. 2020;63:103942. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2020.103942. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

