A comparison of total thoracoscopic versus robotic approach for cardiac myxoma resection: a single-center retrospective study
- PMID: 36648634
- PMCID: PMC10374789
- DOI: 10.1007/s11701-023-01531-z
A comparison of total thoracoscopic versus robotic approach for cardiac myxoma resection: a single-center retrospective study
Abstract
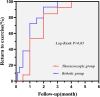
Advances in instrumentation and technique have facilitated minimally invasive surgeries for cardiac myxoma treatment. This study aims to compare the clinical outcomes between the thoracoscopic and robotic approaches for myxoma resection. Intraoperative data and postoperative data of 46 patients who underwent either thoracoscopic (n = 15) or robotic (n = 31) cardiac myxoma resection in our center between July 2013 and September 2022 were retrospectively compared. There was no in-hospital death in either group. Meanwhile, the operative time and cardiopulmonary bypass time were significantly shorter in the robotic group than in thoracoscopic group (P = 0.015 and P = 0.035, respectively). Furthermore, shorter ICU stays (P = 0.006), shorter postoperative mechanical ventilation time (P = 0.035) and less thoracic drainage (P = 0.040) were observed in the robotic group. However, the operating room costs and total hospital costs were both significantly lower in thoracoscopic group (P = 0.004 and P = 0.007, respectively). There was no significant difference between two groups regarding the incidence of postoperative complications (P > 0.05). Lastly, a faster return to exercise was noted in robotic group than in thoracoscopic group (Log-Rank χ2 = 4.094, P = 0.043). Both approaches can be safe and feasible for myxoma resection. However, regardless of higher expenses, the robotic myxoma resection approach provides shorter operation time, less postoperative thoracic drainage, and faster recovery than total thoracoscopic technique.
Keywords: Minimally invasive surgical procedures; Myxoma; Robotics; Thoracoscopy.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

