HDAC7 is an immunometabolic switch triaging danger signals for engagement of antimicrobial versus inflammatory responses in macrophages
- PMID: 36649417
- PMCID: PMC9942870
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2212813120
HDAC7 is an immunometabolic switch triaging danger signals for engagement of antimicrobial versus inflammatory responses in macrophages
Abstract
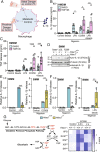
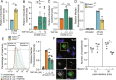
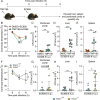
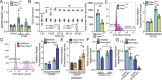
The immune system must be able to respond to a myriad of different threats, each requiring a distinct type of response. Here, we demonstrate that the cytoplasmic lysine deacetylase HDAC7 in macrophages is a metabolic switch that triages danger signals to enable the most appropriate immune response. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and soluble signals indicating distal or far-away danger trigger HDAC7-dependent glycolysis and proinflammatory IL-1β production. In contrast, HDAC7 initiates the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) for NADPH and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in response to the more proximal threat of nearby bacteria, as exemplified by studies on uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC). HDAC7-mediated PPP engagement via 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (6PGD) generates NADPH for antimicrobial ROS production, as well as D-ribulose-5-phosphate (RL5P) that both synergizes with ROS for UPEC killing and suppresses selective inflammatory responses. This dual functionality of the HDAC7-6PGD-RL5P axis prioritizes responses to proximal threats. Our findings thus reveal that the PPP metabolite RL5P has both antimicrobial and immunomodulatory activities and that engagement of enzymes in catabolic versus anabolic metabolic pathways triages responses to different types of danger for generation of inflammatory versus antimicrobial responses, respectively.
Keywords: immunometabolism; inflammation; macrophages; pentose phosphate pathway; uropathogenic Escherichia coli.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- Beutler B., TLR4 as the mammalian endotoxin sensor. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 270, 109–120 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Kayagaki N., et al. , Non-canonical inflammasome activation targets caspase-11. Nature 479, 117–121 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Baker P. J., et al. , NLRP3 inflammasome activation downstream of cytoplasmic LPS recognition by both caspase-4 and caspase-5. Eur. J. Immunol. 45, 2918–2926 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

